Exploring the prognostic impact of absolute lymphocyte count in patients treated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 39516713
- PMCID: PMC11523911
- DOI: 10.1038/s44276-024-00058-6
Exploring the prognostic impact of absolute lymphocyte count in patients treated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
Background: The role of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) expands but affordable and reproducible prognostic biomarkers are needed. We investigated the association between baseline and 3-month absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) and survival for patients on ICI.
Methods: A retrospective study investigated patients who received ICI July 2014-August 2019. Survival probabilities were calculated for lymphocyte subsets. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to investigate risk factors for lymphopenia.
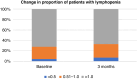
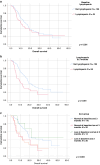
Results: Among 179 patients, median age was 62 and 41% were female. The most common diagnoses were melanoma (41%) and lung cancer (40%). Median PFS was 6.5 months. 27% had baseline lymphopenia (ALC < 1 × 109cells/L) and no significant difference in PFS or OS to those with normal ALC. However, 31% had lymphopenia at 3 months and significantly shorter OS than those without (9.8 vs 18.3 months, p < 0.001). Those with baseline lymphopenia who recovered counts at 3 months had no difference in PFS (median NR vs 13.0 months, p = 0.48) or OS (22 vs 18.3 months, p = 0.548) to those never lymphopenic. The strongest risk factor for lymphopenia on multivariable analysis was previous radiation therapy (RT).
Conclusions: 3-month lymphopenia is a negative prognostic marker in cancer patients on ICI. Previous RT is significantly associated with lymphopenia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RB reports travel funding from Bayer, Janssen, Ipsen, BMS and Pfizer. HOS reports honoraria from Takeda and Amgen. SOR is Deputy Editor of this journal, and recused himself from all decisions about this paper. The other authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Radiation Therapy on Lymphocyte Count and Survival in Metastatic Cancer Patients Receiving PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Jan 1;103(1):142-151. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019. PMID: 30227198
-
Development of Lymphopenia during Therapy with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Is Associated with Poor Outcome in Metastatic Cutaneous Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 5;14(13):3282. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133282. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35805052 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of absolute lymphocyte count in patients with advanced esophageal cancer treated with immunotherapy: a retrospective analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jul;10(13):744. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2669. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35957729 Free PMC article.
-
Hospitalized cancer patients with comorbidities and low lymphocyte counts had poor clinical outcomes to immune checkpoint inhibitors.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 14;12:980181. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.980181. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36185315 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphopenia association with accelerated hyperfractionation and its effects on limited-stage small cell lung cancer patients' clinical outcomes.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Aug;7(16):385. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.07.58. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31555699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith SM, Wachter K, Burris HA 3rd, Schilsky RL, George DJ, et al. Clinical cancer advances 2021: ASCO’s report on progress against cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:1165–84. 10.1200/jco.20.03420. - PubMed
-
- Leighl NB, Nirmalakumar S, Ezeife DA, Gyawali B. An arm and a leg: the rising cost of cancer drugs and impact on access. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2021:e1–e12. 10.1200/edbk_100028. - PubMed
-
- Hodi FS, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob JJ, Rutkowski P, Cowey CL, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab alone versus ipilimumab alone in advanced melanoma (CheckMate 067): 4-year outcomes of a multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:1480–92. 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30700-9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
