Auxiliary effect of trolox on coenzyme Q10 restricts angiogenesis and proliferation of retinoblastoma cells via the ERK/Akt pathway
- PMID: 39516493
- PMCID: PMC11549309
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-76135-0
Auxiliary effect of trolox on coenzyme Q10 restricts angiogenesis and proliferation of retinoblastoma cells via the ERK/Akt pathway
Abstract
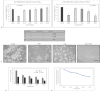
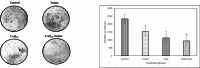
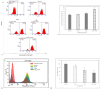
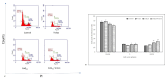
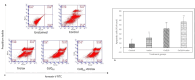
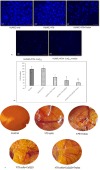
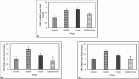
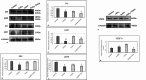
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are essential for cancer signalling pathways and tumour maintenance, making ROS targeting a promising anti-cancer strategy. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) has been shown to be effective against various cancers, but its impact on retinoblastoma, alone or with trolox, remains unreported. Cytotoxicity of CoQ10 alone and with trolox was evaluated in normal human retinal pigment epithelium cells (ARPE-19) and Y79 retinoblastoma cells using CCK-8. Flow cytometry was used to assess apoptosis, cell cycle, ROS, and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). Anti-angiogenic potential was tested using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assays. Mechanistic studies were conducted via RT-PCR and western blotting. CoQ10, alone and with trolox, reduced Y79 cell viability, induced apoptosis through excess ROS generation, and decreased MMP significantly. Both treatments caused G2/M phase cell arrest. The CAM assay showed a significant reduction in endothelial cell proliferation, evidenced by fewer number of co-cultured HUVECs when exposed to CoQ10 or CoQ10 with trolox. The combination of CoQ10 and trolox significantly reduced VEGF-A, ERK, and Akt receptor levels, while CoQ10 alone significantly inhibited ERK and Akt phosphorylation. Together, CoQ10 and trolox reduced protein expression of VEGFA. CoQ10 alone and with trolox, induces apoptosis in Y79 retinoblastoma cells by inhibiting the ERK/Akt pathway and downregulating VEGFA. This study is the first to report the in vitro and in-ovo anti-cancer potential of CoQ10 alone or when combined with trolox, on human retinoblastoma Y79 cells.
Keywords: Anti-cancer; CoQ10; ERK/Akt inhibition; Rb cells; Trolox.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Panax notoginseng saponins induce apoptosis in retinoblastoma Y79 cells via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Mar;216:108954. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.108954. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 35074343
-
Isoindolone derivative QSN-10c induces leukemic cell apoptosis and suppresses angiogenesis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway inhibition.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 May;35(5):625-35. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.194. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 24786233 Free PMC article.
-
OSU-A9 inhibits angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via disrupting Akt-NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 Nov 1;272(3):616-24. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.07.014. Epub 2013 Aug 3. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23921148
-
S-Adenosylmethionine Inhibits the Proliferation of Retinoblastoma Cell Y79, Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of Y79 Cells by Inhibiting the Wnt2/β-Catenin Pathway.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2024 Oct 4;72(1). doi: 10.2478/aite-2024-0020. eCollection 2024 Jan 1. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2024. PMID: 39362212
-
Luteolin inhibits human prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052279. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang, K. et al. Corosolic acid induces cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in human retinoblastoma Y-79 cells via disruption of MELK-FoxM1 signaling. Oncol. Rep. 39(6), 2777–2786. 10.3892/OR.2018.6339/HTML (2018). - PubMed
-
- Zhou, M. et al. Recent progress in retinoblastoma: Pathogenesis, presentation, diagnosis and management. Asia-Pacific J. Ophthalmol. 13(2), 100058. 10.1016/j.apjo.2024.100058 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Correa, Z. M. & Berry, J. L. Review of retinoblastoma-American Academy of Ophthalmology. https://www.aao.org/education/disease-review/review-of-retinoblastoma (Accessed 21 Mar 2023).
-
- Pai, V. et al. Diagnostic IMaGING for retinoblastoma cancer staging: guide for providing essential insights for ophthalmologists and oncologists. RadioGraphics 44(4), e230125. 10.1148/rg.230125 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

