Mechanosensory entities and functionality of endothelial cells
- PMID: 39507419
- PMCID: PMC11538060
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1446452
Mechanosensory entities and functionality of endothelial cells
Abstract
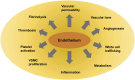
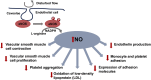
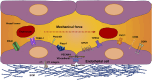
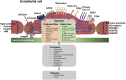
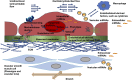
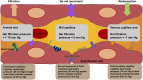
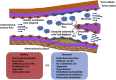
The endothelial cells of the blood circulation are exposed to hemodynamic forces, such as cyclic strain, hydrostatic forces, and shear stress caused by the blood fluid's frictional force. Endothelial cells perceive mechanical forces via mechanosensors and thus elicit physiological reactions such as alterations in vessel width. The mechanosensors considered comprise ion channels, structures linked to the plasma membrane, cytoskeletal spectrin scaffold, mechanoreceptors, and junctional proteins. This review focuses on endothelial mechanosensors and how they alter the vascular functions of endothelial cells. The current state of knowledge on the dysregulation of endothelial mechanosensitivity in disease is briefly presented. The interplay in mechanical perception between endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells is briefly outlined. Finally, future research avenues are highlighted, which are necessary to overcome existing limitations.
Keywords: endothelial cell anisotropy; fluid shear stress; forces; integrins; ion channels; mechanoreceptors; stiffness; vascular function.
Copyright © 2024 Mierke.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial Mechanosignaling: Does One Sensor Fit All?Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Sep 1;25(7):373-88. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6493. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 27027326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial cellular response to altered shear stress.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001 Sep;281(3):L529-33. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2001.281.3.L529. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11504676 Review.
-
Mechanosensing by Vascular Endothelium.Annu Rev Physiol. 2024 Feb 12;86:71-97. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-042022-030946. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Annu Rev Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37863105 Review.
-
Vascular Endothelial Cell Behavior in Complex Mechanical Microenvironments.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018 Nov 12;4(11):3818-3842. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00628. Epub 2018 Nov 1. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018. PMID: 33429612
-
Transient Receptor Potential Channels in Vascular Mechanotransduction.Am J Hypertens. 2024 Nov 23:hpae134. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpae134. Online ahead of print. Am J Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 39579078
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

