High Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Radiodensity Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients With Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 39502618
- PMCID: PMC11534057
- DOI: 10.21873/cdp.10392
High Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Radiodensity Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients With Gastric Cancer
Abstract
Background/aim: Although the impact of body composition on cancer treatment outcomes of patients with cancer has been increasingly reported, it is still unclear whether the radiodensity of subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) on computed tomography (CT) images has a prognostic impact on patients with gastric cancer. We measured muscle and SAT profiles on CT and performed an integrated analysis with clinicopathologic factors.
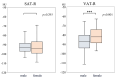
Patients and methods: We retrospectively analyzed 230 patients with gastric cancer who underwent gastrectomy between June 2016 and December 2020. SAT radiodensity (SAT-R), and skeletal muscle index (SMI) were measured in preoperative CT images. These were compared with clinicopathologic factors, overall survival (OS), and recurrence-free survival (RFS).
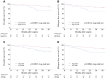
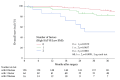
Results: High SAT-R was significantly associated with older age (p=0.003) and lower BMI, lymphocyte, hemoglobin, γ-GTP, cholinesterase, albumin, and triglyceride values (p<0.001, <0.001, 0.027, 0.032, <0.001, 0.001, and <0.001, respectively). In the univariate analysis, high SAT-R, and low SMI were significantly associated with poor OS (p=0.003 and <0.001) and poor RFS (p=0.014 and 0.011). In the multivariate analysis by Cox proportional hazard model, high SAT-R and low SMI were identified as independent prognostic factors for poor OS (p=0.037 and 0.007).
Conclusion: High SAT-R on preoperative CT was associated with poor OS in patients with gastric cancer after gastrectomy. SAT-R has a potential to be a novel prognostic marker for surgically treated patients with gastric cancer.
Keywords: Adipose tissue radiodensity; gastric cancer; skeletal muscle index; survival.
©2024 The Author(s). Published by the International Institute of Anticancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
All Authors declare no conflicts of interest in relation to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor metabolic activity is associated with subcutaneous adipose tissue radiodensity and survival in non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Nutr. 2024 Jul;43(7):1809-1815. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.05.040. Epub 2024 May 28. Clin Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38870661
-
Coexistence of muscle atrophy and high subcutaneous adipose tissue radiodensity predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Nutr. 2023 Oct 6;10:1272728. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1272728. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37867493 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of computed tomography‑derived skeletal muscle index and radiodensity in patients with gastric cancer after curative gastrectomy.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jul 25;28(4):458. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14591. eCollection 2024 Oct. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39114573 Free PMC article.
-
Higher subcutaneous adipose tissue radiodensity is associated with increased mortality in patients with cirrhosis.JHEP Rep. 2022 Apr 27;4(7):100495. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100495. eCollection 2022 Jul. JHEP Rep. 2022. PMID: 35600667 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral adiposity and inflammatory bowel disease.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Nov;36(11):2305-2319. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03968-w. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021. PMID: 34104989 Review.
References
-
- Ito Y, Miwa T, Kanda M, Ito S, Mochizuki Y, Teramoto H, Ishigure K, Murai T, Asada T, Ishiyama A, Matsushita H, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, Fujiwara M, Murotani K, Kodera Y. Risk score for predicting death from other causes after curative gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2023;26(2):317–323. doi: 10.1007/s10120-022-01354-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nunobe S, Oda I, Ishikawa T, Akazawa K, Katai H, Isobe Y, Miyashiro I, Tsujitani S, Ono H, Tanabe S, Fukagawa T, Suzuki S, Kakeji Y, Registration Committee of the Japanese Gastric Cancer Surgical outcomes of elderly patients with Stage I gastric cancer from the nationwide registry of the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Gastric Cancer. 2020;23:328–338. doi: 10.1007/s10120-019-01000-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rinninella E, Cintoni M, Raoul P, Pozzo C, Strippoli A, Bria E, Tortora G, Gasbarrini A, Mele MC. Muscle mass, assessed at diagnosis by L3-CT scan as a prognostic marker of clinical outcomes in patients with gastric cancer: Asystematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Nutrition. 2020;39(7):2045–2054. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.10.021. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
