Prostate neuroendocrine carcinoma successfully treated with etoposide and cisplatin
- PMID: 39498181
- PMCID: PMC11531870
- DOI: 10.1002/iju5.12787
Prostate neuroendocrine carcinoma successfully treated with etoposide and cisplatin
Abstract
Introduction: The frequency of neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate is low, accounting for approximately 1%-5% of all prostate cancers. Herein, we report the case of a patient who was diagnosed with prostate neuroendocrine carcinoma and successfully treated with etoposide and cisplatin.
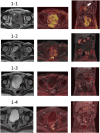
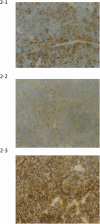
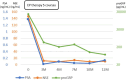
Case presentation: A 74-year-old man presented to the urology department with the chief complaint of urinary retention. After a thorough examination, he was diagnosed with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate and treated with etoposide and cisplatin, called "EP therapy." The patient remained in remission 1 year later.
Conclusion: A patient with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate was successfully treated with etoposide and cisplatin, and the patient remained in remission. Prostate neuroendocrine carcinomas are rare and have poor prognoses. Therefore, information regarding treatments that can improve prognosis is needed.
Keywords: cisplatin; etoposide; metastasis; neuroendocrine carcinoma; prostate.
© 2024 The Author(s). IJU Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Urological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate in a hormone naive patient: A case report from Taiwan.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018 Sep;14(Supplement):S785-S788. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.180685. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30249904
-
De novo large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate gland with pelvic lymph node metastasis: a case report with review of literature.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):9061-6. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment outcome after sequential chemotherapy with cisplatin-etoposide, amrubicin and nogitecan in patients with treatment-related pure small-cell neuroendocrine prostate cancer.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun 1;53(6):522-529. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyad011. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36828781
-
De novo large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate: A case report and literature review.IJU Case Rep. 2022 Aug 30;5(6):505-510. doi: 10.1002/iju5.12527. eCollection 2022 Nov. IJU Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36341182 Free PMC article.
-
[Combined treatment with CDDP and radiation effective against neuroendocrine carcinoma of the urinary bladder: a case report].Hinyokika Kiyo. 1999 Jul;45(7):489-92. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1999. PMID: 10466067 Review. Japanese.
References
-
- Matei DV, Renne G, Pimentel M et al. Neuroendocrine differentiation in castration‐resistant prostate cancer: a systematic diagnostic attempt. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2012; 10: 164–173. - PubMed
-
- Evans AJ, Humphrey PA, Belani J, van der Kwast TH, Srigley JR. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of prostate: a clinicopathologic summary of 7 cases of a rare manifestation of advanced prostate cancer. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006; 30: 684–693. - PubMed
-
- di Sant'Agnese PA. Neuroendocrine differentiation in carcinoma of the prostate. Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications. Cancer 1992; 70: 254–268. - PubMed
-
- Abbas F, Civantos F, Benedetto P, Soloway MS. Small cell carcinoma of the bladder and prostate. Urology 1995; 46: 617–630. - PubMed
-
- Spiess PE, Pettaway CA, Vakar‐Lopez F et al. Treatment outcomes of small cell carcinoma of the prostate: a single‐center study. Cancer 2007; 110: 1729–1737. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
