Involvement of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 in pain insensitivity in a BTBR mouse model of autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 39497100
- PMCID: PMC11533282
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03722-3
Involvement of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 in pain insensitivity in a BTBR mouse model of autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
Background: Abnormal sensory perception, particularly pain insensitivity (PAI), is a typical symptom of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Despite the role of myelin metabolism in the regulation of pain perception, the mechanisms underlying ASD-related PAI remain unclear.
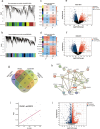
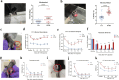
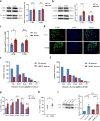
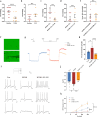
Methods: The pain-associated gene sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1) was identified in ASD samples through bioinformatics analysis. Its expression in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) tissues of BTBR ASD model mice was validated using RNA-seq, western blot, RT-qPCR, and immunofluorescence. Pain thresholds were assessed using the von Frey and Hargreaves tests. Patch-clamp techniques measured KCNQ/M channel activity and neuronal action potentials. The expression of S1PR1, KCNQ/M, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and cyclic AMP/protein kinase A (cAMP/PKA) signaling proteins was analyzed before and after inhibiting the S1P-S1PR1-KCNQ/M pathway via western blot and RT-qPCR.
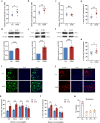
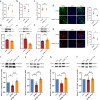
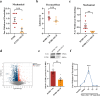
Results: Through integrated transcriptomic analysis of ASD samples, we identified the upregulated gene S1PR1, which is associated with sphingolipid metabolism and linked to pain perception, and confirmed its role in the BTBR mouse model of ASD. This mechanism involves the regulation of KCNQ/M channels in DRG neurons. The enhanced activity of KCNQ/M channels and the decreased action potentials in small and medium DRG neurons were correlated with PAI in a BTBR mouse model of ASD. Inhibition of the S1P/S1PR1 pathway rescued baseline insensitivity to pain by suppressing KCNQ/M channels in DRG neurons, mediated through the MAPK and cAMP/PKA pathways. Investigating the modulation and underlying mechanisms of the non-opioid pathway involving S1PR1 will provide new insights into clinical targeted interventions for PAI in ASD.
Conclusions: S1PR1 may contribute to PAI in the PNS in ASD. The mechanism involves KCNQ/M channels and the MAPK and cAMP/PKA signaling pathways. Targeting S1PR1 in the PNS could offer novel therapeutic strategies for the intervention of pain dysesthesias in individuals with ASD.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorder; BTBR model mice; KCNQ/M potassium channels; Pain insensitivity; Sphingosine-1-phosphate.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Genedrive kit for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism m.1555A>G in neonates and their mothers: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(75):1-75. doi: 10.3310/TGAC4201. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487741 Free PMC article.
-
Ceftazidime with avibactam for treating severe aerobic Gram-negative bacterial infections: technology evaluation to inform a novel subscription-style payment model.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(73):1-230. doi: 10.3310/YAPL9347. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487661 Free PMC article.
-
Zonation and ligand and dose dependence of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 signalling in blood and lymphatic vasculature.Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Nov 25;120(14):1794-1810. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvae168. Cardiovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 39086170
-
Synbiotics, prebiotics and probiotics for people with chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 23;10(10):CD013631. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013631.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37870148 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Robertson CE, Baron-Cohen S. Sensory perception in autism. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18(11):671–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

