Alarin regulates RyR2 and SERCA2 to improve cardiac function in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- PMID: 39494460
- PMCID: PMC11583138
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2024.4122
Alarin regulates RyR2 and SERCA2 to improve cardiac function in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Abstract
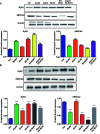
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), a complex disease that is increasingly prevalent due to population aging, pose significant challenges in its treatment. The present study utilized the HFpEF rat model and H9C2 cells as research subjects to thoroughly investigate the potential mechanisms of alarin in protecting cardiac function in HFpEF. The study shows that under HFpEF conditions, oxidative stress significantly increases, leading to myocardial structural damage and dysfunction of calcium ion channels, which ultimately impairs diastolic function. Alarin, through its interaction with NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1), effectively alleviates oxidative stress and modulates the activities of type 2 ryanodine receptor (RyR2) and sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 (SERCA2), thereby facilitating the restoration of Ca2+ homeostasis and significantly improving cardiac function in the HFpEF model. This research not only uncovers the cardioprotective effects of alarin and its underlying molecular mechanisms but also provides new insights and potential therapeutic targets for HFpEF treatment strategies, suggesting a promising future for alarin and related therapies in the management of this debilitating condition.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early calcium handling imbalance in pressure overload-induced heart failure with nearly normal left ventricular ejection fraction.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Jan;1865(1):230-242. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019. PMID: 30463691
-
Malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal adducts are not formed on cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) and sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA2) in diabetes.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Apr;376(1-2):121-35. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1558-1. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23354458 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the peptides Relaxin, Neuregulin, Ghrelin and Glucagon-like peptide-1, on cardiomyocyte factors involved in the molecular mechanisms leading to diastolic dysfunction and/or heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Peptides. 2019 Jan;111:33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.05.009. Epub 2018 May 25. Peptides. 2019. PMID: 29807087 Review.
-
Cardiac diastolic and autonomic dysfunction are aggravated by central chemoreflex activation in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction rats.J Physiol. 2017 Apr 15;595(8):2479-2495. doi: 10.1113/JP273558. Epub 2017 Mar 19. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28181258 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology-based novel pharmacotherapy for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Nov;140(2):156-66. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.05.012. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23792088 Review.
References
-
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Bohm M, et al. . 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 2021;42:3599-726. - PubMed
-
- Pagel PS, Tawil JN, Boettcher BT, Izquierdo DA, Lazicki TJ, Crystal GJ, et al. . Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A comprehensive review and update of diagnosis, pathophysiology, treatment, and perioperative implications. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2021;35:1839-59. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein D, Frishman WH. Diastolic heart failure: a review of current and future treatment options. Cardiol Rev 2021;29:82-8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

