Enhanced susceptibility of pediatric airway epithelium to respiratory syncytial virus infection
- PMID: 39484717
- PMCID: PMC11527439
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI185689
Enhanced susceptibility of pediatric airway epithelium to respiratory syncytial virus infection
Abstract
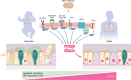
Immature innate and adaptive immunity and vulnerability of narrower airways to obstruction increase the susceptibility of infants to severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease. In this issue of the JCI, Zhao et al. illustrated greater intrinsic susceptibility of pediatric versus adult airway epithelial cells to RSV-induced cytopathology. Using precision cut lung slices (PCLS) and air-liquid interface (ALI) airway epithelial cell cultures, the authors showed that impaired STAT3 activation in RSV-infected pediatric multiciliated cells increased cell apoptosis and viral shedding, which enhanced the spread of infection. Bolstering STAT3 activation and treatment of neonatal mice with apoptosis inhibitors suppressed virus spread, suggesting that enhancing STAT3 activation may provide therapeutic benefit.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
- Activation of STAT3-mediated ciliated cell survival protects against severe infection by respiratory syncytial virus
Similar articles
-
Activation of STAT3-mediated ciliated cell survival protects against severe infection by respiratory syncytial virus.J Clin Invest. 2024 Nov 1;134(21):e183978. doi: 10.1172/JCI183978. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39484716 Free PMC article.
-
Induction and Antagonism of Antiviral Responses in Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Infected Pediatric Airway Epithelium.J Virol. 2015 Dec;89(24):12309-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02119-15. Epub 2015 Sep 30. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26423940 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-Airway Epithelial Interactions Result in Increased Epithelial Damage and Viral Clearance during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection.J Virol. 2020 Jun 16;94(13):e02161-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02161-19. Print 2020 Jun 16. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32295918 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in understanding respiratory syncytial virus infection in airway epithelial cells and consequential effects on the immune response.Microbes Infect. 2013 Mar;15(3):230-42. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2012.11.012. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Microbes Infect. 2013. PMID: 23246463 Review.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus interaction with human airway epithelium.Trends Microbiol. 2013 May;21(5):238-44. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.02.004. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Trends Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23523320 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

