Molecular Interplay in Cardiac Fibrosis: Exploring the Functions of RUNX2, BMP2, and Notch
- PMID: 39484128
- PMCID: PMC11522771
- DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2510368
Molecular Interplay in Cardiac Fibrosis: Exploring the Functions of RUNX2, BMP2, and Notch
Abstract
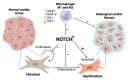
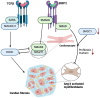
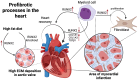
Cardiac fibrosis, characterized by the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, significantly contributes to the morbidity and mortality associated with cardiovascular diseases. This article explores the complex interplay between Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2), and Notch signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. Each of these pathways plays a crucial role in the regulation of cellular functions and interactions that underpin fibrotic processes in the heart. Through a detailed review of current research, we highlight how the crosstalk among RUNX2, BMP2, and Notch not only facilitates our understanding of the fibrotic mechanisms but also points to potential biomolecular targets for intervention. This article delves into the regulatory networks, identifies key molecular mediators, and discusses the implications of these signaling pathways in cardiac structural remodeling. By synthesizing findings from recent studies, we provide insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms that could guide future research directions, aiming to uncover new therapeutic strategies to manage and treat cardiac fibrosis effectively.
Keywords: Notch signaling pathways; Runt-related transcription factor 2; bone morphogenetic protein 2; cardiac fibrosis; signaling interactions.
Copyright: © 2024 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interplay between BMP2 and Notch signaling in endothelial-mesenchymal transition: implications for cardiac fibrosis.Stem Cell Investig. 2023 Sep 28;10:18. doi: 10.21037/sci-2023-019. eCollection 2023. Stem Cell Investig. 2023. PMID: 37842185 Free PMC article.
-
The Complex Interplay of TGF-β and Notch Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 8;25(19):10803. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910803. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory effect of microRNA-21 on pathways and mechanisms involved in cardiac fibrosis development.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2024 Jan-Dec;18:17539447241253134. doi: 10.1177/17539447241253134. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38819836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-specific expression of runt-related transcription factor 2 contributes to pulmonary fibrosis.FASEB J. 2018 Feb;32(2):703-716. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700482R. Epub 2018 Jan 4. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 28986417
-
Canonical Notch signaling is required for bone morphogenetic protein-mediated human osteoblast differentiation.Stem Cells. 2020 Oct 1;38(10):1332-1347. doi: 10.1002/stem.3245. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32535942
References
-
- Al-Hasani J, Hecker M. Cardiac Mechanobiology in Physiology and Disease . Springer International Publishing; Cham: 2023. Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells and Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis; pp. 229–264.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

