The effect of myo-inositol supplementation on AMPK/PI3K/AKT pathway and insulin resistance in patients with NAFLD
- PMID: 39479697
- PMCID: PMC11521746
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.4267
The effect of myo-inositol supplementation on AMPK/PI3K/AKT pathway and insulin resistance in patients with NAFLD
Abstract
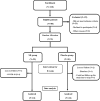
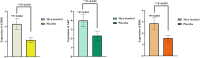
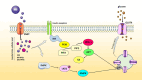
Insulin resistance (IR) is the pivotal pathological hit in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). There is specific attention to combination/conjugated therapies for NAFLD management. As myo-inositol (MI) has been shown to improve IR in animal and human trials, this study aimed to investigate the influence of MI supplementation on glycemic response and IR through AMPK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in obese patients with NAFLD. This double-blinded placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial was conducted on 48 obese (BMI = 30-40 kg/m2) patients with NAFLD who were randomly assigned to receiving either MI (4 g/day) or placebo (maltodextrin 4 g/day) group for 8 weeks. Before and after the trial, weight, height, serum glycemic parameters (inc. fasting glucose and insulin) as well as IR indices were assessed. Moreover, the mRNA expression levels of AMPK, AKT, and PDK-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were determined. MI supplementation resulted in significant increases in the fold changes of AMPK, AKT, and PDK-1 genes (p = .019, p = .049, and p = .029, respectively). Indeed, IR improved in terms of all IR indices in MI group (p < .05) after adjusting for the confounders, apart from quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI). The results showed that MI supplementation not only upregulated AMPK, AKT, and PDK-1 mRNA in PBMCs but also improved IR in obese patients with NAFLD.
Keywords: gene expression; insulin resistance; myo‐inositol; non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2024 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Myo-inositol supplementation improves cardiometabolic factors, anthropometric measures, and liver function in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Nutr. 2023 Feb 7;10:1092544. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1092544. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36824177 Free PMC article.
-
Propolis supplementation in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: effects on glucose homeostasis, lipid profile, liver function, anthropometric indices and meta-inflammation.Food Funct. 2022 Nov 14;13(22):11568-11578. doi: 10.1039/d2fo01280d. Food Funct. 2022. PMID: 36263703 Clinical Trial.
-
Nano-curcumin improves glucose indices, lipids, inflammation, and Nesfatin in overweight and obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019 Jan 28;16:8. doi: 10.1186/s12986-019-0331-1. eCollection 2019. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019. PMID: 30705687 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role and therapeutic interests of myo-inositol in metabolic diseases.Biochimie. 2013 Oct;95(10):1811-27. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 23764390 Review.
-
Understanding Insulin Resistance in NAFLD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Focused on HOMA-IR in South Asians.Cureus. 2024 Oct 3;16(10):e70768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70768. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39364176 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antony, P. J. , Gandhi, G. R. , Stalin, A. , Balakrishna, K. , Toppo, E. , Sivasankaran, K. , Ignacimuthu, S. , & al‐Dhabi, N. A. (2017). Myoinositol ameliorates high‐fat diet and streptozotocin‐induced diabetes in rats through promoting insulin receptor signaling. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 88, 1098–1113. - PubMed
-
- Arefhosseini, S. , Roshanravan, N. , Asghari, S. , Tutunchi, H. , & Ebrahimi‐Mameghani, M. (2023). Expression of inflammatory genes, WBC‐derived inflammatory biomarkers and liver function indices: Effects of myo‐inositol supplementation in obese patients with NAFLD. Journal of Functional Foods, 104, 105524.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

