Targeting sirtuins for cancer therapy: epigenetics modifications and beyond
- PMID: 39479446
- PMCID: PMC11519805
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.100667
Targeting sirtuins for cancer therapy: epigenetics modifications and beyond
Abstract
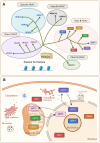
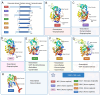
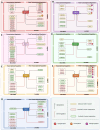
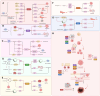
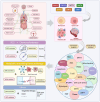
Sirtuins (SIRTs) are well-known as nicotinic adenine dinucleotide+(NAD+)-dependent histone deacetylases, which are important epigenetic enzymes consisting of seven family members (SIRT1-7). Of note, SIRT1 and SIRT2 are distributed in the nucleus and cytoplasm, while SIRT3, SIRT4 and SIRT5 are localized in the mitochondria. SIRT6 and SIRT7 are distributed in the nucleus. SIRTs catalyze the deacetylation of various substrate proteins, thereby modulating numerous biological processes, including transcription, DNA repair and genome stability, metabolism, and signal transduction. Notably, accumulating evidence has recently underscored the multi-faceted roles of SIRTs in both the suppression and progression of various types of human cancers. Crucially, SIRTs have been emerging as promising therapeutic targets for cancer therapy. Thus, in this review, we not only present an overview of the molecular structure and function of SIRTs, but elucidate their intricate associations with oncogenesis. Additionally, we discuss the current landscape of small-molecule activators and inhibitors targeting SIRTs in the contexts of cancer and further elaborate their combination therapies, especially highlighting their prospective utility for future cancer drug development.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Epigenetics modification; Sirtuin (SIRT); Small-molecule activator; Small-molecule inhibitor.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Cancer: A Revisited Review from Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies.Theranostics. 2024 May 11;14(7):2993-3013. doi: 10.7150/thno.97320. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38773972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin family in autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1186231. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1186231. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37483618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuins as Players in the Signal Transduction of Citrus Flavonoids.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 6;25(4):1956. doi: 10.3390/ijms25041956. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on Sirtuins (SIRTs) family modulators.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 May;174:116481. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116481. Epub 2024 Mar 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38522239 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Chronic Degenerative Diseases: New Metabolic Targets in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 16;23(6):3212. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063212. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328633 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oppedisano F, Nesci S, Spagnoletta A. Mitochondrial sirtuin 3 and role of natural compounds: the effect of post-translational modifications on cellular metabolism. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2024;59:199–220. - PubMed
-
- Schwer B, Verdin E. Conserved Metabolic Regulatory Functions of Sirtuins. Cell Metabolism. 2008;7:104–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

