Analyzing the Role of Specific Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns-Related Genes in Osteoarthritis and Investigating the Association between β-Amyloid and Apolipoprotein E Isoforms
- PMID: 39471788
- PMCID: PMC11521507
- DOI: 10.1159/000541542
Analyzing the Role of Specific Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns-Related Genes in Osteoarthritis and Investigating the Association between β-Amyloid and Apolipoprotein E Isoforms
Abstract
Introduction: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent chronic joint disorder. It is characterized by an immune response that maintains a low level of inflammation throughout its progression. During OA, cartilage degradation leads to the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which intensify the inflammatory response. β-Amyloid is a well-recognized DAMP in OA, can interact with APOE isoforms.
Methods: This study identified DAMPs-related genes in OA using bioinformatics techniques. Additionally, we examined the expression levels of β-amyloid and apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoforms by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
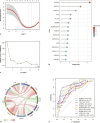
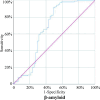
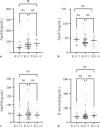
Results: We identified 10 key genes by machine learning techniques. Immune infiltration analysis revealed upregulation of various immune cell types in OA cartilage, underscoring the critical role of inflammation in OA pathogenesis. In the validation study, elevated serum levels of β-amyloid in knee osteoarthritis (KOA) patients were confirmed, showing positive correlations with ApoE2 and ApoE4. Notably, ApoE3 was identified as an independent protective factor against KOA.
Conclusion: In this bioinformatics analysis, we identified the DAMPs-related genes of KOA and explored their potential functions and regulatory networks. The high expression of β-amyloid in KOA was confirmed by experiments, and the correlation between β-amyloid and ApoE2, ApoE4 in KOA was revealed for the first time, this provides a new way to explore the pathogenesis of KOA and to study the therapeutic targets of KOA.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein E; Bioinformatics analysis; Damage-associated molecular patterns; Osteoarthritis; β-Amyloid.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human ApoE Isoforms Differentially Modulate Glucose and Amyloid Metabolic Pathways in Female Brain: Evidence of the Mechanism of Neuroprotection by ApoE2 and Implications for Alzheimer's Disease Prevention and Early Intervention.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;48(2):411-24. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150348. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 26402005 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Netrin-4 Expression and Its Action in Infrapatellar Fat Pad.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 22;25(21):11369. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111369. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39518922 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma ApoE4 Levels Are Lower than ApoE2 and ApoE3 Levels, and Not Associated with Plasma Aβ40/42 Ratio as a Biomarker of Amyloid-β Amyloidosis in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;93(1):333-348. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220996. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 36970894
-
The interaction of amyloid-beta with ApoE.Subcell Biochem. 2005;38:255-72. doi: 10.1007/0-387-23226-5_13. Subcell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15709483 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E isoform-dependent effects on the processing of Alzheimer's amyloid-β.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021 Sep;1866(9):158980. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.158980. Epub 2021 May 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021. PMID: 34044125 Review.
References
-
- Pereira D, Ramos E, Branco J. Osteoarthritis. Acta Med Port. 2015;28(1):99–106. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

