GSK3179106 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and acute lung injury by targeting P38 MAPK
- PMID: 39468539
- PMCID: PMC11520791
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-024-03012-9
GSK3179106 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and acute lung injury by targeting P38 MAPK
Abstract
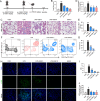
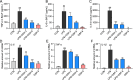
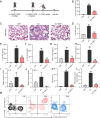
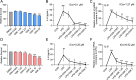
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a serious acute respiratory disease that can cause alveolar-capillary barrier disruption and pulmonary edema, respiratory failure and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. However, there is no effective drugs in clinic until now. GSK3179106 has been reported can alleviate intestinal stress syndrome, but the protective effect of GSK3179106 on ALI has not been elucidated. The present study will evaluate the pharmacological activity of GSK3179106 on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation and lung injury and clarify its underlying mechanism. We found that GSK3179106 significantly attenuated LPS-induced lung injury in vivo, accompanied by inhibited infiltration of inflammatory cells and reduced expression of inflammatory cytokines. Meanwhile, GSK3179106 dose-dependently reduced the LPS-induced IL-6 expression both in protein and gene levels in macrophages. Mechanistically, GSK3179106 could inhibited the phosphorylation of P38 MAPK induced by LPS. Importantly, results showed that there is a direct combination between GSK3179106 and P38 MAPK. Together, our findings not only clarified the anti-inflammatory activity of GSK3179106 but also discovered its new clinical indications. Therefore, compound GSK3179106 may be a potential candidate for the treatment of acute inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; GSK3179106; Lipopolysaccharide; P38 MAPK kinase; Sepsis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zerumbone from Zingiber zerumbet Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced ICAM-1 and Cytokines Expression via p38 MAPK/JNK-IκB/NF-κB Pathway in Mouse Model of Acute Lung Injury.Chin J Physiol. 2018 Jun;61(3):171-180. doi: 10.4077/CJP.2018.BAG562. Chin J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29962177
-
Lower Oligomeric Form of Surfactant Protein D in Murine Acute Lung Injury Induces M1 Subtype Macrophages Through Calreticulin/p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 16;12:687506. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.687506. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484184 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine Supplementation Attenuates the Inflammation Caused by LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice by Regulating the TLR4/MAPK Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2021 Dec;44(6):2180-2192. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01491-2. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 34160729
-
The protective effect of lidocaine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats through NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathway and excessive inflammatory responses.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Apr;22(7):2099-2108. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201804_14743. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29687869
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of novel curcumin analogs in experimental acute lung injury.Respir Res. 2015 Mar 24;16(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0199-1. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 25889862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dellinger RP, et al. Effects of inhaled nitric oxide in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: results of a randomized phase II trial. Inhaled nitric oxide in ARDS study group. Critic Care Med. 1998;26(1):15–23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

