Positions of cysteine residues reveal local clusters and hidden relationships to Sequons and Transmembrane domains in Human proteins
- PMID: 39468182
- PMCID: PMC11519667
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-77056-8
Positions of cysteine residues reveal local clusters and hidden relationships to Sequons and Transmembrane domains in Human proteins
Abstract
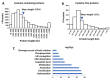
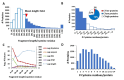
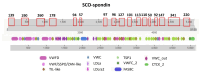
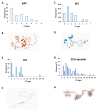
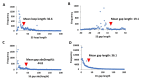
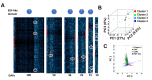
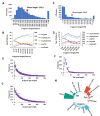
Membrane proteins often possess critical structural features, such as transmembrane domains (TMs), N-glycosylation, and disulfide bonds (SS bonds), which are essential to their structure and function. Here, we extend the study of the motifs carrying N-glycosylation, i.e. the sequons, and the Cys residues supporting the SS bonds, to the whole human proteome with a particular focus on the Cys positions in human proteins with respect to those of sequons and TMs. As the least abundant amino acid residue in protein sequences, the positions of Cys residues in proteins are not random but rather selected through evolution. We discovered that the frequency of Cys residues in proteins is length dependent, and the frequency of CC gaps formed between adjacent Cys residues can be used as a classifier to distinguish proteins with special structures and functions, such as keratin-associated proteins (KAPs), extracellular proteins with EGF-like domains, and nuclear proteins with zinc finger C2H2 domains. Most importantly, by comparing the positions of Cys residues to those of sequons and TMs, we discovered that these structural features can form dense clusters in highly repeated and mutually exclusive modalities in protein sequences. The evolutionary advantages of such complementarity among the three structural features are discussed, particularly in light of structural dynamics in proteins that are lacking from computational predictions. The discoveries made here highlight the sequence-structure-function axis in biological organisms that can be utilized in future protein engineering toward synthetic biology.
Keywords: Cysteine residues; Disulfide bonds; N-glycosylation; Posttranslational modifications; Protein sequence; Protein structure and function; Sequons; Transmembrane domains.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Enabling Systemic Identification and Functionality Profiling for Cdc42 Homeostatic Modulators.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 8:2024.01.05.574351. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.05.574351. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Chem. 2024 Nov 19;7(1):271. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01352-7 PMID: 38260445 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Unlocking data: Decision-maker perspectives on cross-sectoral data sharing and linkage as part of a whole-systems approach to public health policy and practice.Public Health Res (Southampt). 2024 Nov 20:1-30. doi: 10.3310/KYTW2173. Online ahead of print. Public Health Res (Southampt). 2024. PMID: 39582242
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petersen, M.T., P.H. Jonson, and S.B. Petersen, Amino acid neighbours and detailed conformational analysis of cysteines in proteins. Protein Eng, 1999. 12(7): p. 535 − 48. - PubMed
-
- Gupta, R. and S. Brunak, Prediction of glycosylation across the human proteome and the correlation to protein function. Pac Symp Biocomput, 2002: p. 310 − 22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

