Protein kinase D1 in myeloid lineage cells contributes to the accumulation of CXCR3+CCR6+ nonconventional Th1 cells in the lungs and potentiates hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by S. rectivirgula
- PMID: 39464896
- PMCID: PMC11502317
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1403155
Protein kinase D1 in myeloid lineage cells contributes to the accumulation of CXCR3+CCR6+ nonconventional Th1 cells in the lungs and potentiates hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by S. rectivirgula
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Protein kinase D1 in myeloid lineage cells contributes to the accumulation of CXCR3+CCR6+ nonconventional Th1 cells in the lungs and potentiates hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by S. rectivirgula.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 5;15:1513635. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1513635. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39564134 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is an extrinsic allergic alveolitis characterized by inflammation of the interstitium, bronchioles, and alveoli of the lung that leads to granuloma formation. We previously found that activation of protein kinase D1 (PKD1) in the lungs following exposures to Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula contributes to the acute pulmonary inflammation, IL-17A expression in the lungs, and development of HP. In the present study, we investigated whether PKD1 in myeloid-lineage cells affects the pathogenic course of the S. rectivirgula-induced HP.
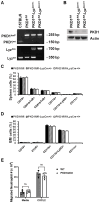
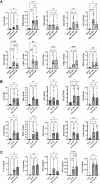
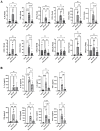
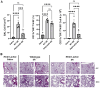
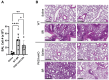
Methods: Mice were exposed intranasally to S. rectivirgula once or 3 times/week for 3 weeks. The protein and mRNA expression levels of cytokines/chemokines were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and quantitative real-time PCR, respectively. Flow cytometry was used to detect the different types of immune cells and the levels of surface proteins. Lung tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, digital images were captured, and immune cells influx into the interstitial lung tissue were detected.
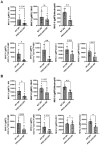
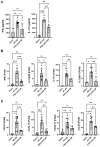
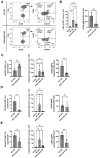
Results: Compared to control PKD1-sufficient mice, mice with PKD1 deficiency in myeloid-lineage cells (PKD1mKO) showed significantly suppressed expression of TNFα, IFNγ, IL-6, CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL10 and neutrophilic alveolitis after single intranasal exposure to S. rectivirgula. Substantially reduced levels of alveolitis and granuloma formation were observed in the PKD1mKO mice repeatedly exposed to S. rectivirgula for 3 weeks. In addition, expression levels of the Th1/Th17 polarizing cytokines and chemokines such as IFNγ, IL-17A, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, and CCL20 in lungs were significantly reduced in the PKD1mKO mice repeatedly exposed to S. rectivirgula. Moreover, accumulation of CXCR3+CCR6+ nonconventional Th1 in the lungs were significantly reduced in PKD1mKO mice repeatedly exposed to S. rectivirgula.
Discussion: Our results demonstrate that PKD1 in myeloid-lineage cells plays an essential role in the development and progress of HP caused by repeated exposure to S. rectivirgula by contributing Th1/Th17 polarizing proinflammatory responses, alveolitis, and accumulation of pathogenic nonconventional Th1 cells in the lungs.
Keywords: Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula; alveolitis; cytokines/chemokines; hypersensitivity pneumonitis; inflammation; protein kinase D1; toll-like receptor signaling.
Copyright © 2024 Snyder, Yoon, Lee, Halder, Fitzpatrick and Yi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contribution of Protein Kinase D1 on Acute Pulmonary Inflammation and Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Induced by Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula.Immunohorizons. 2022 Mar 10;6(3):224-242. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2200017. Immunohorizons. 2022. PMID: 35273098
-
Protein kinase D1 is essential for the proinflammatory response induced by hypersensitivity pneumonitis-causing thermophilic actinomycetes Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula.J Immunol. 2010 Mar 15;184(6):3145-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903718. Epub 2010 Feb 8. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20142359 Free PMC article.
-
Corrigendum: Protein kinase D1 in myeloid lineage cells contributes to the accumulation of CXCR3+CCR6+ nonconventional Th1 cells in the lungs and potentiates hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by S. rectivirgula.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 5;15:1513635. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1513635. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39564134 Free PMC article.
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis and alpha-chemokines.Clin Ter. 2017 Mar-Apr;168(2):e140-e145. doi: 10.7417/CT.2017.1996. Clin Ter. 2017. PMID: 28383627 Review.
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2004 Sep;10(5):401-11. doi: 10.1097/01.mcp.0000135675.95674.29. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2004. PMID: 15316440 Review.
References
-
- Richerson HB, Bernstein IL, Fink JN, Hunninghake GW, Novey HS, Reed CE, et al. . Guidelines for the clinical evaluation of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Report of the Subcommittee on Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (1989) 84:839–44. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90349-7 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

