Differences in Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Transgenic hACE2-Hamster Founder Lines
- PMID: 39459957
- PMCID: PMC11512293
- DOI: 10.3390/v16101625
Differences in Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Transgenic hACE2-Hamster Founder Lines
Abstract
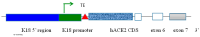
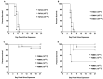
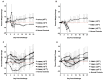
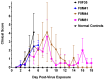
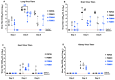
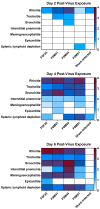
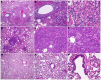
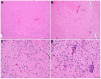
Animal models that are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection and develop clinical signs like human COVID-19 are desired to understand viral pathogenesis and develop effective medical countermeasures. The golden Syrian hamster is important for the study of SARS-CoV-2 since hamsters are naturally susceptible to SARS-CoV-2. However, infected hamsters show only limited clinical disease and resolve infection quickly. In this study, we describe development of human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) transgenic hamsters as a model for COVID-19. During development of the model for SARS-CoV-2, we observed that different hACE2 transgenic hamster founder lines varied in their susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 lethal infection. The highly susceptible hACE2 founder lines F0F35 and F0M41 rapidly progress to severe infection and death within 6 days post-infection (p.i.). Clinical signs included lethargy, weight loss, dyspnea, and mortality. Lethality was observed in a viral dose-dependent manner with a lethal dose as low as 1 × 100.15 CCID50. In addition, virus shedding from highly susceptible lines was detected in oropharyngeal swabs on days 2-5 p.i., and virus titers were observed at 105.5-6.5 CCID50 in lung and brain tissue by day 4 p.i.. Histopathology revealed that infected hACE2-hamsters developed rhinitis, tracheitis, bronchointerstitial pneumonia, and encephalitis. Mortality in highly susceptible hACE2-hamsters can be attributed to neurologic disease with contributions from the accompanying respiratory disease. In contrast, virus challenge of animals from less susceptible founder lines, F0M44 and F0M51, resulted in only 0-20% mortality. To demonstrate utility of this SARS-CoV-2 infection model, we determined the protective effect of the TLR3 agonist polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (Poly (I:C)). Prophylactic treatment with Poly (I:C) significantly improved survival in highly susceptible hACE2-hamsters. In summary, our studies demonstrate that hACE2 transgenic hamsters differ in their susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, based on the transgenic hamster founder line, and that prophylactic treatment with Poly (I:C) was protective in this COVID-19 model of highly susceptible hACE2-hamsters.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; animal model; transgenic hamster; viral pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hamsters Expressing Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Develop Severe Disease following Exposure to SARS-CoV-2.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0290621. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02906-21. Epub 2022 Jan 25. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35073750 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Causes Lung Infection without Severe Disease in Human ACE2 Knock-In Mice.J Virol. 2022 Jan 12;96(1):e0151121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01511-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34668780 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 BA.5.5 and BQ.1.1 Omicron variants in mice and hamsters.J Virol. 2023 Sep 28;97(9):e0062823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00628-23. Epub 2023 Sep 7. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37676002 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV replication and pathogenesis in an in vitro model of the human conducting airway epithelium.Virus Res. 2008 Apr;133(1):33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.03.013. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 17451829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hamsters as a Model of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2.Comp Med. 2021 Oct 1;71(5):398-410. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-21-000036. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Comp Med. 2021. PMID: 34588095 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen N., Zhou M., Dong X., Qu J., Gong F., Han Y., Qiu Y., Wang J., Liu Y., Wei Y., et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 99 Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study. Lancet. 2020;395:507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

