The Potential of Glucosinolates and Their Hydrolysis Products as Inhibitors of Cytokine Storms
- PMID: 39459194
- PMCID: PMC11510469
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29204826
The Potential of Glucosinolates and Their Hydrolysis Products as Inhibitors of Cytokine Storms
Abstract
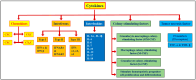
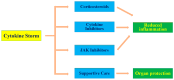
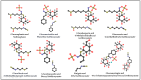
A cytokine storm is an intense inflammatory response characterized by the overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines, resulting in tissue damage, and organ dysfunction. Cytokines play a crucial role in various conditions, such as coronavirus disease, in which the immune system becomes overactive and releases excessive levels of cytokines, including interleukins, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). This anomalous response often leads to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), and multiple organ injury (MOI). Glucosinolates are plant secondary metabolites predominantly found in Brassica vegetables, but are also present in other species, such as Moringa Adens and Carica papaya L. When catalyzed by the enzyme myrosinase, glucosinolates produce valuable products, including sulforaphane, phenethyl isothiocyanate, 6-(methylsulfinyl) hexyl isothiocyanate, erucin, goitrin, and moringin. These hydrolyzed products regulate proinflammatory cytokine production by inhibiting the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cell (NF-κB) signaling pathway and stimulating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathway. This action can alleviate hyperinflammation in infected cells and modulate cytokine storms. In this review, we aimed to examine the potential role of glucosinolates in modulating cytokine storms and reducing inflammation in various conditions, such as coronavirus disease. Overall, we found that glucosinolates and their hydrolysis products can potentially attenuate cytokine production and the onset of cytokine storms in diseased cells. In summary, glucosinolates could be beneficial in regulating cytokine production and preventing complications related to cytokine storms.
Keywords: NF-κB; TNF-α; cytokine storm; enzymatic hydrolysis; glucosinolates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucosinolates and their hydrolysis products as potential nutraceuticals to combat cytokine storm in SARS-COV-2.Daru. 2022 Jun;30(1):245-252. doi: 10.1007/s40199-022-00435-x. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Daru. 2022. PMID: 35112323 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Carcinogenic Glucosinolates in Cruciferous Vegetables and Their Antagonistic Effects on Prevention of Cancers.Molecules. 2018 Nov 15;23(11):2983. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112983. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30445746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Glucosinolates Hydrolytic Products in Neurodegenerative Diseases (NDDs).Nutrients. 2018 May 8;10(5):580. doi: 10.3390/nu10050580. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29738500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucosinolates in cancer prevention and treatment: experimental and clinical evidence.Med Oncol. 2023 Nov 3;40(12):344. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02211-6. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37921869 Review.
-
Effects of β-Blockers on the Sympathetic and Cytokines Storms in Covid-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 11;12:749291. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.749291. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34867978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

