Akkermansia muciniphila for the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies
- PMID: 39458436
- PMCID: PMC11510203
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16203440
Akkermansia muciniphila for the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies
Abstract
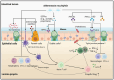
Background: More than half of the states in the U.S. report that over 30% of adults are obese. Obesity increases the risk of many chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease, and can even reduce one's lifespan. Similarly, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes follows a comparable trend. As a result, researchers are striving to find solutions to reduce obesity rates, with a particular focus on gut health, which has been previously linked to both obesity and type 2 diabetes. Recent studies suggest that Akkermansia muciniphila (Akk) may have a positive probiotic effect on preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes and obesity.
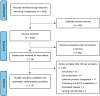
Methods: We conducted a quantitative meta-analysis of 15 qualified animal studies investigating the effects of Akk administration as a probiotic.
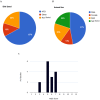
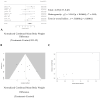
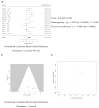
Results: The statistical analyses showed that Akk administration significantly reduced body weight gain by 10.4% and fasting blood glucose by 21.2%, while also significantly improving glucose tolerance by 22.1% and increasing blood insulin levels by 26.9%. However, our analysis revealed substantial heterogeneity between the control and experimental groups across all subgroups.
Conclusions: Overall, Akk appears to be effective at reducing the onset of type 2 diabetes and diet-induced obesity. Long-term studies with larger sample sizes are needed to confirm these beneficial effects, as the current animal studies were of short duration (less than 20 weeks).
Keywords: Akkermansia; animals; meta-analysis; obesity; probiotic; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protective effects of Akkermansia muciniphila on cognitive deficits and amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Nutr Diabetes. 2020 Apr 22;10(1):12. doi: 10.1038/s41387-020-0115-8. Nutr Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32321934 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila in Alleviating Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Jun 12;72(23):13083-13098. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c01188. Epub 2024 Jun 3. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38829529
-
Influence of oral administration of Akkermansia muciniphila on the tissue distribution and gut microbiota composition of acute and chronic cadmium exposure mice.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019 Jul 1;366(13):fnz160. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnz160. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31310663
-
Akkermansia muciniphila: A promising probiotic against inflammation and metabolic disorders.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2375555. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2375555. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39192579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of Literature on Akkermansia muciniphila and its Possible Role in the Etiopathogenesis and Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2022;37(1):69-74. doi: 10.15605/jafes.037.01.13. Epub 2022 Apr 21. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2022. PMID: 35800592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dao M.C., Everard A., Aron-Wisnewsky J., Sokolovska N., Prifti E., Verger E.O., Kayser B.D., Levenez F., Chilloux J., Hoyles L., et al. Akkermansia muciniphila and Improved Metabolic Health During a Dietary Intervention in Obesity: Relationship with Gut Microbiome Richness and Ecology. Gut. 2016;65:426–436. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308778. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

