Predictive Value of Monocyte-To-Lymphocyte Ratio in Differentiating Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis-A Retrospective Analysis
- PMID: 39458199
- PMCID: PMC11508807
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13206249
Predictive Value of Monocyte-To-Lymphocyte Ratio in Differentiating Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis-A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
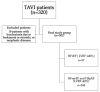
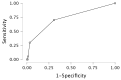
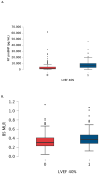
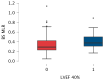
Background/Objectives: Advanced calcific aortic stenosis, with or without coronary artery disease [CAD], may lead to severe systolic dysfunction. The aim of the study was to reveal clinical and laboratory parameters that may differentiate patients with severe aortic stenosis with and without systolic dysfunction. Methods: A retrospective, single-center study included all consecutive patients diagnosed with severe aortic stenosis with overt heart failure. Patients with hematological and neoplastic diseases were excluded. Demographic, clinical and laboratory data were analysed. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte [NLR], monocyte-to-lymphocyte [MLR], and platelet-to-lymphocyte [PLR] ratios were calculated. The study group was divided based on left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF]. Results: The final study population comprised 301 patients [133 males [44%]; median [Q1-3] age of 80 [75-83] years]. Co-morbidities included CAD [48.8%], arterial hypertension [75.4%], diabetes mellitus [n = 124, 41.2%], atrial fibrillation [39.2%], chronic kidney disease [60.8%]. Fifty-seven patients presented with LVEF ≤ 40% (heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)) and 244 with LVEF > 40%. In the multivariable analysis, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide [NTproBNP] [p < 0.001, OR 1.000, 95%CI 1.000-1.000], baseline MLR [p < 0.020, OR 7.393, 95%CI 1.363-40.091] and female sex [p < 0.001, OR 0.308, 95%CI 0.160-0.593] were revealed as significant predictors of HFrEF. Baseline MLR weakly correlated with EuroScore II [Spearman r = 0.141, p = 0.015] and NTproBNP [r = 0.142, p = 0.014]. Cut-off values were established as 0.36 for MLR and 3927 pg/mL for NTproBNP. After excluding 147 patients with CAD, there was still a statistically significant difference in MLR between the subgroups [p = 0.024]. Conclusions: Increased values of MLR and NTproBNP together with female sex are predictive parameters for LVEF ≤ 40% in patients with severe aortic stenosis.
Keywords: HFrEF; MLR; aortic stenosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between subclinical left ventricular ejection fraction and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with peritoneal dialysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 1;9:961453. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.961453. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36530903 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio associated with 28-day all-cause mortality in septic patients with coronary artery disease: a retrospective analysis of MIMIC-IV database.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jul 29;24(1):749. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09516-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39075364 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of transcatheter aortic valve replacement in elderly people with severe aortic stenosis with different types of heart failure.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Jan 18;23(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03048-7. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 36653770 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and calcific aortic stenosis.Echocardiography. 2014 Oct;31(9):1031-5. doi: 10.1111/echo.12534. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Echocardiography. 2014. PMID: 24528173
-
SGLT2 inhibitor therapy in patients with advanced heart failure and reduced ejection fraction.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Nov;49(11):102823. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102823. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39208997 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

