Comprehensive Analysis of a Platelet- and Coagulation-Related Prognostic Gene Signature Identifies CYP19A1 as a Key Tumorigenic Driver of Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 39457539
- PMCID: PMC11505370
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12102225
Comprehensive Analysis of a Platelet- and Coagulation-Related Prognostic Gene Signature Identifies CYP19A1 as a Key Tumorigenic Driver of Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Background: The intricate interplay between the platelet-coagulation system and the progression of malignant tumors has profound therapeutic implications. However, a thorough examination of platelet and coagulation markers specific to colorectal cancer (CRC) is conspicuously absent in the current literature. Consequently, there is an urgent need for further exploration into the mechanistic underpinnings of these markers and their potential clinical applications.
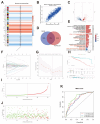
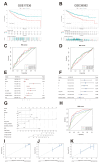
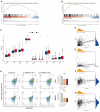
Methods: By integrating RNA-seq data and clinicopathological information from patients with CRC in the cancer genome atlas, we identified genes related to the platelet-coagulation system using weighted gene co-expression networks and univariate Cox analysis. We established a prognostic risk model based on platelet- and coagulation-related genes using Lasso Cox regression analysis and validated the model in two independent CRC cohorts. We explored potential biological functional disparities between high-risk and low-risk groups through comprehensive bioinformatics analysis.
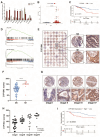
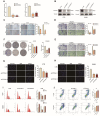
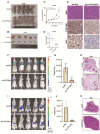
Results: Our findings indicate that colorectal cancer patients classified as high-risk generally exhibit poorer prognoses. Moreover, the model's risk scores were associated with the differential composition of the immune tumor microenvironment, suggesting its applicability to infer immunotherapy responsiveness. Cellular functional experiments and animal experiments indicated that CYP19A1 expression in CRC influences malignant phenotype and platelet activation.
Conclusions: In summary, we present a novel platelet- and coagulation-related risk model for prognostic assessment of patients with CRC and confirm the important role of CYP19A1 in promoting malignant progression of CRC.
Keywords: CYP19A1; coagulation; colorectal cancer; platelet; prognosis; single-cell sequencing; survival; weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computational identification and clinical validation of a novel risk signature based on coagulation-related lncRNAs for predicting prognosis, immunotherapy response, and chemosensitivity in colorectal cancer patients.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 19;14:1279789. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1279789. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37928532 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and verification of prognostic model and ceRNA network analysis for colorectal cancer liver metastasis.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 May 9;16(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01523-w. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37161577 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a New Ferroptosis-related Prognosis Model for Survival Prediction in Colorectal Cancer.Curr Med Chem. 2024 Feb 14. doi: 10.2174/0109298673296767240116215814. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38362684
-
Construction of an immune gene expression meta signature to assess the prognostic risk of colorectal cancer patients.Adv Genet. 2024;112:207-254. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2024.08.005. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Adv Genet. 2024. PMID: 39396837
-
Comprehensive analysis of basement membrane-related gene based on single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing data to predict prognosis and evaluate immune characteristics in colorectal cancer.Environ Toxicol. 2024 Jun;39(6):3367-3380. doi: 10.1002/tox.24211. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Environ Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38445432
References
-
- Gaedcke J., Grade M., Camps J., Søkilde R., Kaczkowski B., Schetter A.J., Difilippantonio M.J., Harris C.C., Ghadimi B.M., Møller S., et al. The rectal cancer microRNAome—microRNA expression in rectal cancer and matched normal mucosa. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18:4919–4930. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 81602145 and 82072704/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BE2021747/Jiangsu Primary Research & Development Plan
- ZT202118/Jiangsu Province TCM Science and Technology Development Plan Monographic Project
- BK20171509/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- QNRC2016649/Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent, The Project of Invigorating Health Care through Science, Technology Education
- 2018M632265/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- BRA2020390/The "333 Talents" Program of Jiangsu Province, Grant/Award Number
- 2017-33/The Talents Program of Jiangsu Cancer Hospital
- CXZX202224/Jiangsu Province Capability Improvement Project through Science, Technology and Education, Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

