Thymine DNA glycosylase combines sliding, hopping, and nucleosome interactions to efficiently search for 5-formylcytosine
- PMID: 39455577
- PMCID: PMC11512004
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53497-7
Thymine DNA glycosylase combines sliding, hopping, and nucleosome interactions to efficiently search for 5-formylcytosine
Abstract
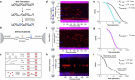
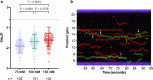
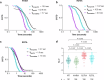
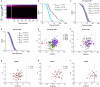
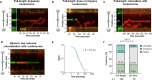
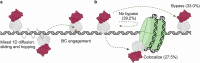
Base excision repair is the main pathway involved in active DNA demethylation. 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine, two oxidized moieties of methylated cytosine, are recognized and removed by thymine DNA glycosylase (TDG) to generate an abasic site. Using single molecule fluorescence experiments, we study TDG in the presence and absence of 5-formylcytosine. TDG exhibits multiple modes of linear diffusion, including hopping and sliding, in search of base modifications. TDG active site variants and truncated N-terminus, reveals these variants alter base modification search and recognition mechanism of TDG. On DNA containing an undamaged nucleosome, TDG is found to either bypass, colocalize with, or encounter but not bypass the nucleosome. Truncating the N-terminus reduces the number of interactions with the nucleosome. Our findings provide mechanistic insights into how TDG searches for modified DNA bases in chromatin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Thymine DNA glycosylase combines sliding, hopping, and nucleosome interactions to efficiently search for 5-formylcytosine.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 27:2023.10.04.560925. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.04.560925. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 25;15(1):9226. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53497-7 PMID: 37873231 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Thymine DNA glycosylase combines sliding, hopping, and nucleosome interactions to efficiently search for 5-formylcytosine.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 27:2023.10.04.560925. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.04.560925. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 25;15(1):9226. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53497-7 PMID: 37873231 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Excision of 5-hydroxymethyluracil and 5-carboxylcytosine by the thymine DNA glycosylase domain: its structural basis and implications for active DNA demethylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Nov 1;40(20):10203-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks845. Epub 2012 Sep 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22962365 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis for Excision of 5-Formylcytosine by Thymine DNA Glycosylase.Biochemistry. 2016 Nov 15;55(45):6205-6208. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00982. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27805810 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications in DNA could mimic oxidative DNA damage: A double-edged sword.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Aug;32:52-57. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.04.013. Epub 2015 May 1. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25956859 Review.
-
Structural and mutation studies of two DNA demethylation related glycosylases: MBD4 and TDG.Biophysics (Nagoya-shi). 2014 Oct 18;10:63-8. doi: 10.2142/biophysics.10.63. eCollection 2014. Biophysics (Nagoya-shi). 2014. PMID: 27493500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35GM128562/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- F32ES034982/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS)
- R35 ES031638/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R35-GM136225/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R35ES031638/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS)
- T32 GM088119/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 ES034982/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM128562/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM088119/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- S10 OD032158/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM136225/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10OD032158-01A1/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | NIH Office of the Director (OD)
- P30 CA047904/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32GM140718/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- F32 GM140718/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

