The Causal Effect of Urate Level on Female Infertility: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- PMID: 39452897
- PMCID: PMC11509567
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo14100516
The Causal Effect of Urate Level on Female Infertility: A Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
Background/objective: This study aimed to investigate the causal relationship between urate level and female infertility using Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.
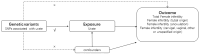
Methods: To identify instrumental variables, we selected independent genetic loci associated with serum urate levels in individuals of European ancestry, utilizing data from large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWAS). The GWAS dataset included information on serum urate levels from 288,649 CKDGen participants. Female infertility data, including different etiologic classifications, consisted of 13,142 female infertility patients and 107,564 controls. We employed four MR methods, namely inverse variance weighted (IVW), MR-Egger, weighted median, and weighted model, to investigate the causal relationship between urate levels and female infertility. The Cochran Q-test was used to assess heterogeneity among single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), and the MR-Egger intercept test was employed to evaluate the presence of horizontal pleiotropy. Additionally, a "leave-one-out" sensitivity analysis was conducted to examine the influence of individual SNPs on the MR study.
Results: The IVW analysis demonstrated that elevated serum urate levels increased the risk of female infertility (odds ratio [OR] = 1.18, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.07-1.33). Furthermore, serum urate levels were found to be associated with infertility due to cervical, vaginal, or other unknown causes (OR = 1.16, 95% CI: 1.06-1.26), also confirmed by other methods. Heterogeneity among instrumental variables was assessed using Cochran's Q-test (p < 0.05), so a random-effects IVW approach was employed in the effects model. The MR-Egger intercept test indicated no presence of horizontal pleiotropy. A "leave-one-out" sensitivity analysis was conducted, demonstrating that no individual SNP had a substantial impact on the overall findings.
Conclusions: In the European population, the urate level is significantly and causally associated with an increased risk of female infertility.
Keywords: causal inference; female infertility; mendelian randomization; urate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Genetic Causation Analysis of Hyperandrogenemia Testing Indicators and Preeclampsia].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):566-573. doi: 10.12182/20240560106. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948277 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Genetic causal relationship between age at menarche and benign oesophageal neoplasia identified by a Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 21;14:1113765. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1113765. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37025412 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic causal relationship between type 2 diabetes, glycemic traits and venous thromboembolism, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Thromb J. 2024 Mar 29;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12959-024-00600-z. Thromb J. 2024. PMID: 38553747 Free PMC article.
-
No evidence of genetic causal association between sex hormone-related traits and systemic lupus erythematosus: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Dec;42(12):3237-3249. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06700-x. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37495778
-
Liposomes have a direct effect on multiple myeloma: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 11;14:1404744. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1404744. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38933448 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Underlying Effect of Urate Levels on Female Infertility.Metabolites. 2024 Oct 21;14(10):564. doi: 10.3390/metabo14100564. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39452945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Y., Fu Y., Ghazi P., Gao Q., Tian T., Kong F., Zhan S., Liu C., Bloom D.E., Qiao J. Prevalence of intimate partner violence against infertile women in low-income and middle-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health. 2022;10:e820–e830. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00098-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

