Back to the Origin: Mechanisms of circRNA-Directed Regulation of Host Genes in Human Disease
- PMID: 39452835
- PMCID: PMC11510700
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna10050049
Back to the Origin: Mechanisms of circRNA-Directed Regulation of Host Genes in Human Disease
Abstract
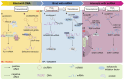
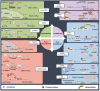
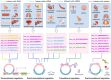
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been shown to be pivotal regulators in various human diseases by participating in gene splicing, acting as microRNA (miRNA) sponges, interacting with RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), and translating into short peptides. As the back-splicing products of pre-mRNAs, many circRNAs can modulate the expression of their host genes through transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational control via interaction with other molecules. This review provides a detailed summary of these regulatory mechanisms based on the class of molecules that they interact with, which encompass DNA, mRNA, miRNA, and RBPs. The co-expression of circRNAs with their parental gene productions (including linear counterparts and proteins) provides potential diagnostic biomarkers for multiple diseases. Meanwhile, the different regulatory mechanisms by which circRNAs act on their host genes via interaction with other molecules constitute complex regulatory networks, which also provide noticeable clues for therapeutic strategies against diseases. Future research should explore whether these proven mechanisms can play a similar role in other types of disease and clarify further details about the cross-talk between circRNAs and host genes. In addition, the regulatory relationship between circRNAs and their host genes in circRNA circularization, degradation, and cellular localization should receive further attention.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; ceRNA; circular RNA; host gene; regulatory mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circular RNAs: Biomarkers of cancer.Cancer Innov. 2022 Sep 21;1(3):197-206. doi: 10.1002/cai2.28. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cancer Innov. 2022. PMID: 38089761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome wide identification and characterization of fertility associated novel CircRNAs as ceRNA reveal their regulatory roles in sheep fecundity.J Ovarian Res. 2023 Jun 20;16(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01178-2. J Ovarian Res. 2023. PMID: 37340323 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Serum Exosome-Derived circRNA-miRNA-TF-mRNA Regulatory Network in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Using Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation in Peripheral Blood-Derived Mononuclear Cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 9;13:899503. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.899503. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35757392 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: An important part of circRNA maintenance and function.J Neurosci Res. 2020 Jan;98(1):87-97. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24356. Epub 2018 Dec 21. J Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 30575990 Review.
-
Understanding the roles and regulation patterns of circRNA on its host gene in tumorigenesis and tumor progression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 15;42(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02657-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37060016 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

