Characterization of Collaborative Cross mouse founder strain CAST/EiJ as a novel model for lethal COVID-19
- PMID: 39448712
- PMCID: PMC11502910
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-77087-1
Characterization of Collaborative Cross mouse founder strain CAST/EiJ as a novel model for lethal COVID-19
Abstract
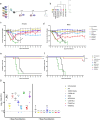
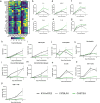
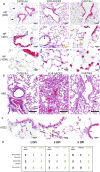
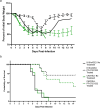
Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) have expanded the viral host range beyond primates, and a few other mammals, to mice, affording the opportunity to exploit genetically diverse mouse panels to model the broad spectrum of responses to infection in patient populations. Here we surveyed responses to VOC infection in genetically diverse Collaborative Cross (CC) founder strains. Infection of wild-derived CC founder strains produced a broad range of viral burden, disease susceptibility and survival, whereas most other strains were resistant to disease despite measurable lung viral titers. In particular, CAST/EiJ, a wild-derived strain, developed high lung viral burdens, more severe lung pathology than seen in other CC strains, and a dysregulated cytokine profile resulting in morbidity and mortality. These inbred mouse strains may serve as a valuable platform to evaluate therapeutic countermeasures against severe COVID-19 and other coronavirus pandemics in the future.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Characterization of Collaborative Cross mouse founder strain CAST/EiJ as a novel model for lethal COVID-19.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 29:rs.3.rs-4675061. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4675061/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 24;14(1):25147. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77087-1. PMID: 39149485 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Characterization of Collaborative Cross mouse founder strain CAST/EiJ as a novel model for lethal COVID-19.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 29:rs.3.rs-4675061. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4675061/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 24;14(1):25147. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77087-1. PMID: 39149485 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Influenza H3N2 infection of the collaborative cross founder strains reveals highly divergent host responses and identifies a unique phenotype in CAST/EiJ mice.BMC Genomics. 2016 Feb 27;17:143. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2483-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26921172 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Causes Lung Infection without Severe Disease in Human ACE2 Knock-In Mice.J Virol. 2022 Jan 12;96(1):e0151121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01511-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34668780 Free PMC article.
-
The Collaborative Cross mouse model for dissecting genetic susceptibility to infectious diseases.Mamm Genome. 2018 Aug;29(7-8):471-487. doi: 10.1007/s00335-018-9768-1. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Mamm Genome. 2018. PMID: 30143822 Review.
-
Omicron: What Makes the Latest SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern So Concerning?J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0207721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02077-21. Epub 2022 Mar 23. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35225672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fauci, A. S. & Folkers, G. K. Pandemic preparedness and response: lessons from COVID-19. J. Infect. Dis.228, 422–425. 10.1093/infdis/jiad095 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

