Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4: A keystone in immune modulation and therapeutic target in cancer and beyond
- PMID: 39444949
- PMCID: PMC11495969
- DOI: 10.1002/cai2.153
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4: A keystone in immune modulation and therapeutic target in cancer and beyond
Abstract
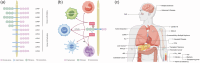
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4 (LILRB4) significantly impacts immune regulation and the pathogenesis and progression of various cancers. This review discusses LILRB4's structural attributes, expression patterns in immune cells, and molecular mechanisms in modulating immune responses. We describe the influence of LILRB4 on T cells, dendritic cells, NK cells, and macrophages, and its dual role in stimulating and suppressing immune activities. The review discusses the current research on LILRB4's involvement in acute myeloid leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and solid tumors, such as colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and extramedullary multiple myeloma. The review also describes LILRB4's role in autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and other conditions. We evaluate the recent advancements in targeting LILRB4 using monoclonal antibodies and peptide inhibitors and their therapeutic potential in cancer treatment. Together, these studies underscore the need for further research on LILRB4's interactions in the tumor microenvironment and highlight its importance as a therapeutic target in oncology and for future clinical innovations.
Keywords: cancer therapy; immune checkpoint; immunotherapy; leukocyte immunoglobulin‐like receptor B4; monoclonal antibodies.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Innovation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Tsinghua University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LILRB4, an immune checkpoint on myeloid cells.Blood Sci. 2022 May 17;4(2):49-56. doi: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000109. eCollection 2022 Apr. Blood Sci. 2022. PMID: 35957669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LILRB4 Checkpoint for Immunotherapy: Structure, Mechanism and Disease Targets.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 4;14(2):187. doi: 10.3390/biom14020187. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain, as a potential immune checkpoint target for immunotherapy of colorectal cancer.IUBMB Life. 2021 May;73(5):726-738. doi: 10.1002/iub.2461. Epub 2021 Mar 30. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 33686787 Review.
-
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B1 and B4 (LILRB1 and LILRB4): Highly sensitive and specific markers of acute myeloid leukemia with monocytic differentiation.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2021 Jul;100(4):476-487. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.21952. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2021. PMID: 32918786
-
LILRB4, from the immune system to the disease target.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Jul 15;12(7):3149-3166. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32774691 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources