The influence of sex on neuroimmune communication, pain, and physiology
- PMID: 39439003
- PMCID: PMC11494817
- DOI: 10.1186/s13293-024-00660-w
The influence of sex on neuroimmune communication, pain, and physiology
Abstract
With the National Institutes of Health's mandate to consider sex as a biological variable (SABV), there has been a significant increase of studies utilizing both sexes. Historically, we have known that biological sex and hormones influence immunological processes and now studies focusing on interactions between the immune, endocrine, and nervous systems are revealing sex differences that influence pain behavior and various molecular and biochemical processes. Neuroendocrine-immune interactions represent a key integrative discipline that will reveal critical processes in each field as it pertains to novel mechanisms in sex differences and necessary therapeutics. Here we appraise preclinical and clinical literature to discuss these interactions and key pathways that drive cell- and sex-specific differences in immunity, pain, and physiology.
Keywords: Hormones; Neuroimmune; Pain; Physiology; Sex differences; Translational.
Plain language summary
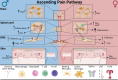
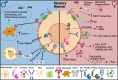
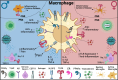
In the last decade, NIH-funded basic and clinical research studies have been mandated to include sex as a biological variable, and this has resulted in a boom of studies discovering sex differences. We know that females are more likely than males to develop chronic pain conditions and experience higher levels of pain for longer periods of time. Conditions that demonstrate this include migraine, arthritis, and peripheral neuropathy. Furthermore, these sex differences extend to surgical outcomes and are observable at the molecular, cellular, and systemic levels. Although pain perception pathways differ by sex, studies are also focusing on differences in the “conversation” between the immune system and the nervous system while addressing implications of sex hormones to gain a better understanding of the impact on pain, physiology, and behavior. Lifestyle factors such as diet and alcohol consumption also play a role in affecting the perception and impact of pain conditions. As this area of research continues to grow, the development and availability of sex-specific treatment options will grow and lead to improved patient outcomes and more effective pain management strategies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors (Alexander, S.N, Green, A.R., Debner, E.K., Abdelhadi, H.M.K., Ramos Freitas, L.E., Szabo-Pardi, T.A., Burton, M.D) have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sensory Neurons, Neuroimmunity, and Pain Modulation by Sex Hormones.Endocrinology. 2021 Aug 1;162(8):bqab109. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab109. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 34049389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Sex as a Biological Variable Still Being Ignored in Preclinical Aging Research?J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022 Nov 21;77(11):2177-2180. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glac042. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35172335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences in pain along the neuraxis.Neuropharmacology. 2022 Jun 1;210:109030. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109030. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Neuropharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35331712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reporting and misreporting of sex differences in the biological sciences.Elife. 2021 Nov 2;10:e70817. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70817. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34726154 Free PMC article.
-
Considering Sex as a Biological Variable in Basic and Clinical Studies: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement.Endocr Rev. 2021 May 25;42(3):219-258. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnaa034. Endocr Rev. 2021. PMID: 33704446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kourounakis P, Selye H. Influence of steroids and stress on toxicity and disposition of tetraethylammonium bromide. J Pharm Sci. 1976;65:12:1838–40. 10.1002/jps.2600651236. - PubMed
-
- Hadamitzky M, Lückemann L, Pacheco-López G, Schedlowski M. Pavlovian conditioning of immunological and neuroendocrine functions. Physiol Rev. 2020;100:1:357–405. 10.1152/physrev.00033.2018. - PubMed
-
- Kourounakis P, Szabo S, Selye H. Effect of pregnenolone-16alpha-carbonitrile on the rat liver. Arzneimittelforschung. 1976;26(1):74–5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/947184. - PubMed
-
- Du Ruisseau P, Tache Y, Selye H, Ducharme JR, Collu R. Effects of chronic stress on pituitary hormone release induced by combined hemi-extirpation of the thyroid, adrenal and ovary in rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1977;24:3–4. 10.1159/000122707. - PubMed
-
- Salas M, Tuchweber B, Kourounakis P, Selye H. Temperature-dependence of stress-induced hepatic autophagy. Experientia. 1977;33:5:612–4. 10.1007/BF01946531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

