MEK inhibition prevents CAR-T cell exhaustion and differentiation via downregulation of c-Fos and JunB
- PMID: 39438476
- PMCID: PMC11496645
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-024-01986-y
MEK inhibition prevents CAR-T cell exhaustion and differentiation via downregulation of c-Fos and JunB
Abstract
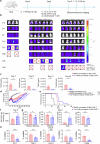
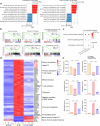
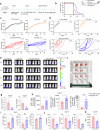
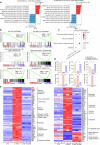
Clinical evidence supports the notion that T cell exhaustion and terminal differentiation pose challenges to the persistence and effectiveness of chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T) cells. MEK1/2 inhibitors (MEKIs), widely used in cancer treatment due to their ability to inhibit aberrant MAPK signaling, have shown potential synergistic effects when combined with immunotherapy. However, the impact and mechanisms of MEKIs on CAR-T cells remain uncertain and controversial. To address this, we conducted a comprehensive investigation to determine whether MEKIs enhance or impair the efficacy of CAR-T cells. Our findings revealed that MEKIs attenuated CAR-T cell exhaustion and terminal differentiation induced by tonic signaling and antigen stimulation, thereby improving CAR-T cell efficacy against hematological and solid tumors. Remarkably, these effects were independent of the specific scFvs and costimulatory domains utilized in CARs. Mechanistically, analysis of bulk and single-cell transcriptional profiles demonstrates that the effect of MEK inhibition was related to diminish anabolic metabolism and downregulation of c-Fos and JunB. Additionally, the overexpression of c-Fos or JunB in CAR-T cells counteracted the effects of MEK inhibition. Furthermore, our Cut-and-Tag assay revealed that MEK inhibition downregulated the JunB-driven gene profiles associated with exhaustion, differentiation, anergy, glycolysis, and apoptosis. In summary, our research unveil the critical role of the MAPK-c-Fos-JunB axis in driving CAR-T cell exhaustion and terminal differentiation. These mechanistic insights significantly broaden the potential application of MEKIs to enhance the effectiveness of CAR-T therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dasatinib enhances anti-leukemia efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T cells by inhibiting cell differentiation and exhaustion.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jul 21;14(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01117-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34289897 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of CAR-Mediated Tonic Signaling.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2086:223-236. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0146-4_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31707680
-
Improving CAR-T immunotherapy: Overcoming the challenges of T cell exhaustion.EBioMedicine. 2022 Mar;77:103941. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103941. Epub 2022 Mar 15. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35301179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Bearing Herpes Virus Entry Mediator Co-Stimulatory Signal Domain Exhibits Exhaustion-Resistant Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 8;25(16):8662. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168662. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201348 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the ability of CAR-T cells to hit solid tumors: Challenges and strategies.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Jan;175:106036. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.106036. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 34920118 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

