Single-chain A35R-M1R-B6R trivalent mRNA vaccines protect mice against both mpox virus and vaccinia virus
- PMID: 39423738
- PMCID: PMC11513793
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105392
Single-chain A35R-M1R-B6R trivalent mRNA vaccines protect mice against both mpox virus and vaccinia virus
Abstract
Background: Mpox has spread to many countries around the world. While the existing live attenuated mpox vaccines are effective, advances in 21st century technologies now enable the development of vaccines with more specific antigens, clearer mechanisms, and more controllable side effects.
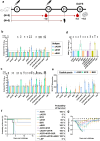
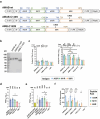
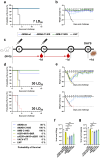
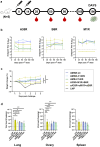
Methods: We systematically evaluated the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of the A35R, M1R and B6R antigens of the mpox virus (MPXV). With these findings, we designed three single-chain trivalent mRNA vaccines (AMAB-wt, AMAB-C140S and AMB-C140S) by integrating the soluble regions of these antigens into single mRNA-encoded polypeptides based on their protein structures. Then, the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of these single-chain mRNA vaccines were evaluated in mice models against both VACV and MPXV.
Findings: The three single-chain vaccines elicited neutralising antibodies that effectively neutralised both VACV and MPXV. The single-chain vaccines or cocktail vaccine containing mRNAs encoding soluble antigen (sA35R + sM1R + sB6R) exhibited 100% or 80% protection against a lethal dose of VACV challenge, while the cocktail of full-length antigens (A35 + M1 + B6) and the live attenuated vaccine, VACV Tian Tan (VACV-VTT), completely failed to protect mice. Moreover, the single-chain vaccines significantly reduced viral load in the lungs and ovaries of MPXV-challenged mice.
Interpretation: Compared with the cocktail vaccines, our single-chain designs demonstrated similar or superior immunogenicity and protective efficacy. Importantly, the simplicity of the single-chain vaccines enhances both the controllability and accessibility of mpox vaccines. We believe these single-chain vaccines qualify as the next-generation mpox vaccines.
Funding: National Natural Science Foundation of China and Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the CAS.
Keywords: Chimeric; Single-chain; Trivalent; mRNA vaccine; mpox.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests G.F.G., Q.W., P.D., T.K., and R.M. are listed as inventors on patent applications for the three trivalent mpox mRNA vaccines. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-Lasting Protection and Dose Optimization of MPXV Polyvalent Mpox mRNA Vaccines Against Lethal Vaccinia Virus Challenge in Mice.J Med Virol. 2025 Jan;97(1):e70143. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70143. J Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 39726255
-
Different immunogens and prime-boost vaccination strategies affect the efficacy of recombinant candidate vaccines against pathogenic orthopoxviruses.Virol J. 2024 Nov 7;21(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02534-4. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39511612 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic evaluation of the induction of efficient neutralizing antibodies by recombinant multicomponent subunit vaccines against monkeypox virus.Vaccine. 2024 Dec 2;42(26):126384. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.126384. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 39321566
-
Mpox global health emergency: Insights into the virus, immune responses, and advancements in vaccines PART II: Insights into the advancements in vaccines.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2024 Sep;42(3):191-206. doi: 10.12932/AP-111024-1946. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39417768 Review.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

