Development and validation of a web-based nomogram for acute kidney injury in acute non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding patients
- PMID: 39421858
- PMCID: PMC11484005
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1474311
Development and validation of a web-based nomogram for acute kidney injury in acute non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding patients
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and serious complication in patients with acute non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding (NVUGIB). Early prediction and intervention are crucial for improving patient outcomes.
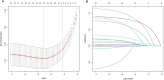
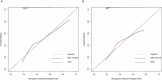
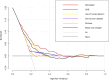
Methods: Data for patients presenting with acute NVUGIB in this retrospective study were sourced from the MIMC-IV database. Patients were randomly allocated into training and validation cohorts for further analysis. Independent predictors for AKI were identified using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression and multivariable logistic regression analyses in the training cohort. Based on the logistic regression results, a nomogram was developed to predict early AKI onset in acute NVUGIB patients, and implemented as a web-based calculator for clinical application. The nomogram's performance was evaluated through discrimination, using the C-index, calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA) to assess its clinical value.
Results: The study involved 1082 acute NVUGIB patients, with 406 developing AKI. A multivariable logistic regression identified five key AKI predictors: CKD, use of human albumin, chronic liver disease, glucose, and blood urea nitrogen. The nomogram was constructed based on independent predictors. The nomogram exhibited robust accuracy, evidenced by a C-index of 0.73 in the training cohort and 0.72 in the validation cohort. Calibration curves demonstrated satisfactory concordance between predicted and observed AKI occurrences. DCA revealed that the nomogram offered considerable clinical benefit within a threshold probability range of 7% to 54%.
Conclusion: Our nomogram is a valuable tool for predicting AKI risk in patients with acute NVUGIB, offering potential for early intervention and improved clinical outcomes.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; intensive care unit; nomogram; prediction; upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
Copyright © 2024 Wei, Cao, Huang and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Construction and evaluation of a mortality prediction model for patients with acute kidney injury undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy based on machine learning algorithms.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2388709. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2388709. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39155811 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a dynamic online nomogram for predicting acute kidney injury in cirrhotic patients upon ICU admission.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 27;10:1055137. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1055137. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36778740 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a dynamic nomogram for short-term survival in acute heart failure patients with acute kidney injury upon ICU admission.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 18;10(20):e39494. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39494. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39502227 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of prognostic nomogram for cirrhotic patients with acute kidney injury upon ICU admission.Intern Emerg Med. 2024 Jan;19(1):49-58. doi: 10.1007/s11739-023-03436-z. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Intern Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 37796371 Clinical Trial.
-
A nomogram incorporating functional and tubular damage biomarkers to predict the risk of acute kidney injury for septic patients.BMC Nephrol. 2021 May 13;22(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02388-w. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33985459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kellum J, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, Ronco C, Zarbock A, Anders H. Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Prim. (2021) 7:52. - PubMed
-
- Ronco C, Bellomo R, Kellum J. Acute kidney injury. Lancet. (2019) 394:1949–64. - PubMed
-
- Cakmak U, Merhametsiz O, Gok Oguz E, Ercan Z, Haspulat A, Ozkan S, et al. Effects of acute kidney injury on clinical outcomes in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Ren Fail. (2016) 38:176–84. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

