This is a preprint.
HHIP's Dynamic Role in Epithelial Wound Healing Reveals a Potential Mechanism of COPD Susceptibility
- PMID: 39416045
- PMCID: PMC11482804
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.05.611545
HHIP's Dynamic Role in Epithelial Wound Healing Reveals a Potential Mechanism of COPD Susceptibility
Abstract
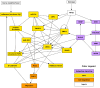
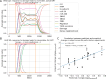
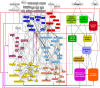
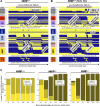
A genetic variant near HHIP has been consistently identified as associated with increased risk for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), the third leading cause of death worldwide. However HHIP's role in COPD pathogenesis remains elusive. Canonically, HHIP is a negative regulator of the hedgehog pathway and downstream GLI1 and GLI2 activation. The hedgehog pathway plays an important role in wound healing, specifically in activating transcription factors that drive the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), which in its intermediate state (partial EMT) is necessary for the collective movement of cells closing the wound. Herein, we propose a mechanism to explain HHIP's role in faulty epithelial wound healing, which could contribute to the development of emphysema, a key feature of COPD. Using two different Boolean models compiled from the literature, we show dysfunctional HHIP results in a lack of negative feedback on GLI, triggering a full EMT, where cells become mesenchymal and do not properly close the wound. We validate these Boolean models with experimental evidence gathered from published scientific literature. We also experimentally test if low HHIP expression is associated with EMT at the edge of wounds by using a scratch assay in a human lung epithelial cell line. Finally, we show evidence supporting our hypothesis in bulk and single cell RNA-Seq data from different COPD cohorts. Overall, our analyses suggest that aberrant wound healing due to dysfunctional HHIP, combined with chronic epithelial damage through cigarette smoke exposure, may be a primary cause of COPD-associated emphysema.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest In the past three years, EKS has received grant support from Bayer and Northpond Laboratories.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hedgehog pathway and its inhibitors in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Dec;240:108295. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108295. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36191777 Review.
-
Identification of a distal enhancer regulating hedgehog interacting protein gene in human lung epithelial cells.EBioMedicine. 2024 Mar;101:105026. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105026. Epub 2024 Feb 27. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38417378 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of hedgehog interacting protein in colorectal cancer: a study based on GEO data and TCGA data.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Aug 11;23(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02867-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37568084 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog interacting protein (HHIP) represses airway remodeling and metabolic reprogramming in COPD-derived airway smooth muscle cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 27;11(1):9074. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88434-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33907231 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in COPD induced by cigarette smoke: an update.Respir Res. 2022 Aug 31;23(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02153-z. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 36045410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adeloye D., Song P., Zhu Y., Campbell H., Sheikh A., Rudan I., NIHR RESPIRE Global Respiratory Health Unit, Global, regional, and national prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in 2019: a systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Respir Med 10, 447–458 (2022). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agustí A., Hogg J. C., Update on the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 381, 1248–1256 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Hogg J. C., Chu F., Utokaparch S., Woods R., Elliott W. M., Buzatu L., Cherniack R. M., Rogers R. M., Sciurba F. C., Coxson H. O., Paré P. D., The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 2645–2653 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Zhou X., Baron R. M., Hardin M., Cho M. H., Zielinski J., Hawrylkiewicz I., Sliwinski P., Hersh C. P., Mancini J. D., Lu K., Thibault D., Donahue A. L., Klanderman B. J., Rosner B., Raby B. A., Lu Q., Geldart A. M., Layne M. D., Perrella M. A., Weiss S. T., Choi A. M. K., Silverman E. K., Identification of a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease genetic determinant that regulates HHIP. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 1325–1335 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
