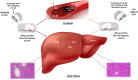
Hepatoprotective effect of Nobiletin against 5-fluorouracil induce hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 39411523
- PMCID: PMC11474214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphar.2024.100199
Hepatoprotective effect of Nobiletin against 5-fluorouracil induce hepatotoxicity
Abstract
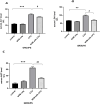
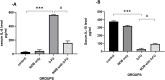
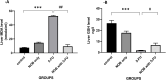
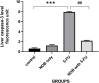
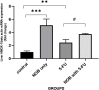
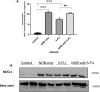
5-florouracil is a widely used anticancer/anti-metabolite drug used to treat solid tumor like colon cancer, head and neck, rectum, stomach, pancreas and breast cancer; but, it can cause hepatotoxicity by induction of apoptosis through activation of caspases enzymes and oxidative stress. Nobiletin is a citrus fruit-derived flavonoid that possess significant biological activity, including anticancer, and anti-inflammatory. This study was design to investigate the effects of nobiletin against 5-florouracil-indcued hepatotoxicity in male rats through the measurement of selected -inflammatory, -apoptosis, and -oxidative stress markers. By use male Albino rats weighing 150-250gm around 28 animals; giving them tap water ad libitum and fed commercial pellets; and randomized into four groups (7animals/group) as following arrangement: Group I oral administered only corn oil for rats 1 ml for each kilogram for day by using of oral gavage for rat for 14 days. Group II: oral administered Nobiletin at dose 10 mg for each kilogram for each day (dissolved in corn oil) via oral gavage for 14 days. Group III: oral administered corn oil via oral gavage for 14 days after that single IP injection of 5-FU (150 mg/kg) on the day fourteenth (14). Group VI: Rats oral administered nobiletin dissolved in corn oil daily by oral gavage at a dose 10 mg/kg for each day for 14 days and a single IP injection of (150 mg/kg) 5-florouracil was given on day 14. All groups, seven animals of each group were sacrificed at day fifteenth (15); and, serum was collected to measure inflammatory and anti-inflammatory markers (interlukin-6 and interlukin-10) and liver function tests(ALT, LDH and AST); furthermore, liver tissue samples were collected to measure level of caspase-3, malondialdehyde and reduced form of glutathione, assessment of Hemeoxygenase-1 and NADPH quinone dehydrogenase-1 enzymes. In addition, histopathological study of the liver tissue of rats was perform to detect difference between architecture of liver cells in all rats' groups. The protective effect of Nobiletin noted by decrease in apoptosis of hepatocytes by decreasing of caspase-3 and reduction on free radical through reduce in malondialdehyde level, also increase in Hemeoxygenase-1gene expression. Increase in NADPH quinone dehydrogenase-1 dehydrogenase enzyme. On histopath reduce in congestion and some inflammatory infiltration by using of nobiletin prior to give 5-florouracil.
Keywords: 5-FU; Caspase-3; Corn oil; HMOX-1; Hepatotoxicity; Nobiletin effect.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Pentachloroanisole (CAS No. 1825-21-4) in F344 Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Feed Studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1993 Apr;414:1-284. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1993. PMID: 12616284
-
NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Coumarin (CAS No. 91-64-5) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1993 Sep;422:1-340. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1993. PMID: 12616289
-
Role of Platelet-activating factor and HO-1 in mediating the protective effect of rupatadine against 5-fluorouracil-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Jun;29(26):40190-40203. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-18899-4. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35119631 Free PMC article.
-
Nobiletin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury due to its anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2015 Jul-Aug;67(7-8):427-33. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2015.04.008. Epub 2015 May 19. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26002685
-
Nobiletin attenuates acetaminophen-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020 Feb;34(2):e22427. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22427. Epub 2019 Nov 27. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31777137
References
-
- Abdul-Azeez Zahraa Maan, Mutlag Shihab Hattab. Possible protective anticancer effect of chloroform fraction of Iraqi Hibiscus tiliaceus L. leaves extract on diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in male rats. J. Compl. Integr. Med. 2024;21(2):167–174. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2023-0290. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdul-Wahab F.K., Al-Shawi N.N. Effects of vitamin D3 on methotrexate-induced jejunum damage in rats. Iraqi J. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2020:260–267. doi: 10.31351/VOL29ISS1PP260-267. - DOI
-
- Abd Al-Zahra J.I., Ismael D.K., Al-Shawi N.N. Preventive effects of different doses of Pentoxyfilline against CCl4-induced liver toxicity in rats. Iraqi J. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2017:39–45. doi: 10.31351/vol18isssuppl. - DOI
-
- Al-Geam Manal A.I., Al-Shawi Nada N. Effects of vitamin E and Q10 supplementation against doxorubicin-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Iraqi J. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2018;27(2):24–31. doi: 10.31351/vol27iss2pp24-31. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

