Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance in Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Activating the FGF21-Adiponectin Axis
- PMID: 39408777
- PMCID: PMC11476820
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910447
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance in Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Activating the FGF21-Adiponectin Axis
Abstract
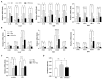
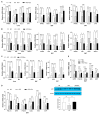
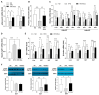
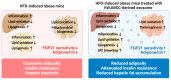
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells have shown promise in treating metabolic disorders, yet their specific mechanisms remain largely unclear. This study investigates the protective effects of exosomes from human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells (hWJMSCs) against adiposity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice. HFD-fed mice treated with hWJMSC-derived exosomes demonstrated improved gut barrier integrity, which restored immune balance in the liver and adipose tissues by reducing macrophage infiltration and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. Furthermore, these exosomes normalized lipid metabolism including lipid oxidation and lipogenesis, which alleviate lipotoxicity-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, thereby decreasing fat accumulation and chronic tissue inflammation in hepatic and adipose tissues. Notably, hWJMSC-derived exosomes also promoted browning and thermogenic capacity of adipose tissues, which was linked to reduced fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) resistance and increased adiponectin production. This process activated the AMPK-SIRT1-PGC-1α pathway, highlighting the role of the FGF21-adiponectin axis. Our findings elucidate the molecular mechanisms through which hWJMSC-derived exosomes counteract HFD-induced metabolic dysfunctions, supporting their potential as therapeutic agents for metabolic disorders.
Keywords: FGF21; SIRT1; adiponectin; exosome; hepatic steatosis; insulin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatic stearoyl CoA desaturase 1 deficiency increases glucose uptake in adipose tissue partially through the PGC-1α-FGF21 axis in mice.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 20;294(51):19475-19485. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009868. Epub 2019 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31690632 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic SIRT1 attenuates hepatic steatosis and controls energy balance in mice by inducing fibroblast growth factor 21.Gastroenterology. 2014 Feb;146(2):539-49.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.10.059. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24184811 Free PMC article.
-
Artemisia scoparia extract attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in diet-induced obesity mice by enhancing hepatic insulin and AMPK signaling independently of FGF21 pathway.Metabolism. 2013 Sep;62(9):1239-49. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 May 21. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23702383 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary capsaicin reduces obesity-induced insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in obese mice fed a high-fat diet.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010 Apr;18(4):780-7. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.301. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010. PMID: 19798065
-
Hydrodynamic delivery of FGF21 gene alleviates obesity and fatty liver in mice fed a high-fat diet.J Control Release. 2014 Jul 10;185:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.03.047. Epub 2014 Apr 18. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24747761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moayedfard Z., Sani F., Alizadeh A., Lankarani K.B., Zarei M., Azarpira N. The role of the immune system in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and potential therapeutic impacts of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022;13:242. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02929-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

