Cancer cell membrane-coated siRNA-Decorated Au/MnO2 nanosensitizers for synergistically enhanced radio-immunotherapy of breast cancer
- PMID: 39403312
- PMCID: PMC11471673
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101275
Cancer cell membrane-coated siRNA-Decorated Au/MnO2 nanosensitizers for synergistically enhanced radio-immunotherapy of breast cancer
Abstract
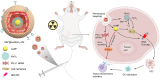
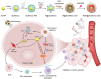
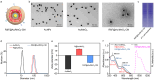
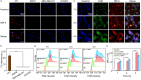
Radiotherapy plays a critical role in the clinical treatment of breast cancer. However, the efficacy of traditional X-ray radiotherapy is greatly limited by its low tumor specificity and treatment tolerance mediated by the tumor microenvironment. Herein, we proposed a novel nano-radiotherapy sensitization strategy to design and construct a cancer cell membrane-coated siRNA-decorated Au/MnO2 nanosensitizer (R&F@Au/MnO2-CM) to synergistically enhance radio-immunotherapy for breast cancer. In the integrated nanosensitizer, the cancer cell membrane (CM) derived from 4T1 breast cancer cells is utilized for targeted functionality, while Au/MnO2 is designed to improve X-ray absorption and alleviate tumor hypoxia. Additionally, PD-L1 siRNA (R) is used to downregulate PD-L1 expression in tumor cells. In an in situ mouse model of 4T1 breast cancer, R&F@Au/MnO2-CM demonstrated accurate tumor identification via CM-mediated homologous targeting after intravenous injection, which was monitored in real-time through NIR-II fluorescence imaging of NIR-935 (F). Subsequently, the radiotherapy sensitivity was achieved due to the strong radiation absorption properties and oxygen generation through catalysis of Au/MnO2 upon X-ray irradiation. Furthermore, the immunosuppressive microenvironment of the tumor is improved by downregulating PD-L1, enhancing synergistic anti-tumor effect. Our findings demonstrate a promising approach for tumor treatment by combining targeted enhanced radiotherapy with immune activation.
Keywords: NIR-II fluorescence; Nanosensitizer; Radiotherapy; Tumor therapy.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pd@Au Bimetallic Nanoplates Decorated Mesoporous MnO2 for Synergistic Nucleus-Targeted NIR-II Photothermal and Hypoxia-Relieved Photodynamic Therapy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2020 Jan;9(2):e1901528. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201901528. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020. PMID: 31820854
-
Reprogramming exosomes for immunity-remodeled photodynamic therapy against non-small cell lung cancer.Bioact Mater. 2024 May 21;39:206-223. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.05.030. eCollection 2024 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38827172 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviating the hypoxic tumor microenvironment with MnO2-coated CeO2 nanoplatform for magnetic resonance imaging guided radiotherapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Mar 15;21(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01850-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 36922836 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic reprogramming mediated PD-L1 depression and hypoxia reversion to reactivate tumor therapy.J Control Release. 2022 Dec;352:793-812. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.11.004. Epub 2022 Nov 11. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 36343761
-
Polyethylene glycol–coated gold nanoshells conjugated with anti-VCAM-1 antibody.2013 Feb 28 [updated 2013 May 16]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2013 Feb 28 [updated 2013 May 16]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23700638 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Frankenberg-Schwager M. Review of repair kinetics for DNA damage induced in eukaryotic cells in vitro by ionizing radiation. Radiother. Oncol. 1989;14(4):307–320. - PubMed
-
- Favourable and unfavourable effects on long-term survival of radiotherapy for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group. Lancet. 2000;355(9217):1757–1770. - PubMed
-
- Wang K., Tepper J.E. Radiation therapy-associated toxicity: etiology, management, and prevention. CA Cancer. J. Clin. 2021;71(5):437–454. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

