Elevated serum IL-17 A and CCL20 levels as potential biomarkers in major psychotic disorders: a case-control study
- PMID: 39394574
- PMCID: PMC11468266
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-024-06032-3
Elevated serum IL-17 A and CCL20 levels as potential biomarkers in major psychotic disorders: a case-control study
Abstract
Background: Major psychotic disorders (MPD), including schizophrenia (SCZ) and schizoaffective disorder (SAD), are severe neuropsychiatric conditions with unclear causes. Understanding their pathophysiology is essential for better diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Recent research highlights the role of inflammation and the immune system, particularly the Interleukin 17 (IL-17) family, in these disorders. Elevated IL-17 levels have been found in MPD, and human IL-17 A antibodies are available. Changes in chemokine levels, such as CCL20, are also noted in SCZ. This study investigates the relationship between serum levels of IL-17 A and CCL20 in MPD patients and their clinical characteristics.
Method: We conducted a case-control study at the Ibn Sina Psychiatric Hospital (Mashhad, Iran) in 2023. The study involved 101 participants, of which 71 were MPD patients and 30 were healthy controls (HC). The Positive and Negative Symptom Scale (PANSS) was utilized to assess the symptoms of MPD patients. Serum levels of CCL20 and IL-17 A were measured using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) kits. We also gathered data on lipid profiles and Fasting Blood Glucose (FBS).
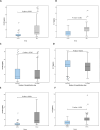
Results: The mean age of patients was 41.04 ± 9.93 years. The median serum levels of CCL20 and IL-17 A were significantly elevated in MPD patients compared to HC (5.8 (4.1-15.3) pg/mL and 4.2 (3-5) pg/mL, respectively; p < 0.001). Furthermore, CCL20 and IL-17 A levels showed a positive correlation with the severity of MPD. MPD patients also had significantly higher FBS, cholesterol, and Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) levels, and lower High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) levels compared to HC. No significant relationship was found between PANSS components and blood levels of IL17 and CCL20.
Conclusion: The current study revealed that the serum levels of IL-17 A and CCL20 in schizophrenia patients are higher than those in the control group. Metabolic factors such as FBS, cholesterol, HDL, and LDL also showed significant differences between MPD and HC. In conclusion, the findings suggest that these two inflammatory factors could serve as potential therapeutic targets and prognostic biomarkers for schizophrenia.
Keywords: CCL20; IL-17A; Major psychotic disorders; PANSS; Schizoaffective disorder; Schizophrenia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum CCL20 combined with IL-17A as early diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for human colorectal cancer.J Transl Med. 2019 Aug 6;17(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-2008-y. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31387598 Free PMC article.
-
Common and disorder-specific upregulation of the inflammatory markers TRAIL and CCL20 in depression and schizophrenia.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 28;11(1):19204. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98769-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34584171 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma levels of chemokine ligand 20 and chemokine receptor 6 in patients with sepsis: A case control study.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2016 May;33(5):348-55. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000388. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2016. PMID: 26771764
-
Electroencephalographic delta/alpha frequency activity differentiates psychotic disorders: a study of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and methamphetamine-induced psychotic disorder.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Apr 12;8(1):75. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0105-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29643331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-analysis of the association between N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antibodies and schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder.Schizophr Res. 2014 Aug;157(1-3):249-58. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Schizophr Res. 2014. PMID: 24882425 Review.
References
-
- Shojaeimotlagh V, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Iranian patients with schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Volume 13. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews; 2019. pp. 143–7. 1. - PubMed
-
- Petrova N, et al. Clinical and immunological profile of patients with schizophrenia. Eur Psychiatry. 2022;65(S1):S105–6.
-
- Lang FU, et al. Subtyping schizophrenia: a comparison of positive/negative and system-specific approaches. Compr Psychiatr. 2015;61:115–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

