Hypoxic reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus
- PMID: 39391006
- PMCID: PMC11466537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellin.2024.100200
Hypoxic reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus
Abstract
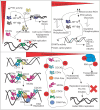
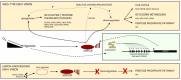
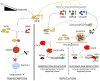
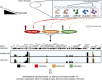
Hypoxic reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) refers to the phenomenon under low oxygen where the virus goes from latent to lytic replication. Typically, healthy cells generally cease cell division and DNA replication under hypoxic conditions due to limited resources, and the presence of physiological inhibitors. This restricted replication under hypoxic conditions is considered an employed strategy of the cell to minimize energy consumption. However, cancerous cells continuously replicate and divide in hypoxic conditions by reprogramming several aspects of their cell physiology, including but not limited to metabolism, cell cycle, DNA replication, transcription, translation, and the epigenome. KSHV infection, similar to cancerous cells, is known to bypass hypoxia-induced restrictions and undergo reactivation to produce progeny viruses. In previous studies we have mapped several aspects of cell physiology that are manipulated by KSHV through its latent antigens during hypoxic conditions, which allows for a permissive environment for its replication. We discuss the major strategies utilized by KSHV to bypass hypoxia-induced repression. We also describe the KSHV-encoded antigens responsible for modulating these cellular processes important for successful viral replication and persistence in hypoxia.
Keywords: Epigenetics; Hypoxia; KSHV; LANA; Reactivation; Replication; Transcription.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIF1α-Regulated Expression of the Fatty Acid Binding Protein Family Is Important for Hypoxic Reactivation of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus.J Virol. 2021 May 24;95(12):e02063-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02063-20. Print 2021 May 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33789996 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of KAP1 enhances hypoxia-induced Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus reactivation through RBP-Jκ.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(12):6873-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00283-14. Epub 2014 Apr 2. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24696491 Free PMC article.
-
Full-Length Isoforms of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency-Associated Nuclear Antigen Accumulate in the Cytoplasm of Cells Undergoing the Lytic Cycle of Replication.J Virol. 2017 Nov 30;91(24):e01532-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01532-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28978712 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivation and Lytic Replication of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus: An Update.Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 20;8:613. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00613. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28473805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of KSHV Latency and Lytic Reactivation.Viruses. 2020 Sep 17;12(9):1034. doi: 10.3390/v12091034. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32957532 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barasa A.K., Ye P., Phelps M., Arivudainambi G.T., Tison T., Ogembo J.G. BALB/c mice immunized with a combination of virus-like particles incorporating Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) envelope glycoproteins gpK8.1, gB, and gH/gL induced comparable serum neutralizing antibody activity to UV-inactivated KSHV. Oncotarget. 2017;8(21):34481–34497. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15605. PubMed PMID: 28404899; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC5470984. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

