Preventive and treatment efficiency of dendrosomal nano-curcumin against ISO-induced cardiac fibrosis in mouse model
- PMID: 39388499
- PMCID: PMC11469592
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311817
Preventive and treatment efficiency of dendrosomal nano-curcumin against ISO-induced cardiac fibrosis in mouse model
Abstract
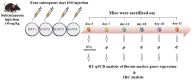
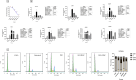
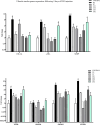
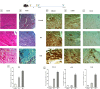
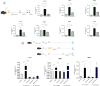
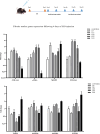
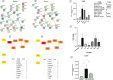
Cardiac fibrosis (c-fibrosis) is a critical factor in cardiovascular diseases, leading to impaired cardiac function and heart failure. This study aims to optimize the isoproterenol (ISO)-induced c-fibrosis model and evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of dendrosomal nano-curcumin (DNC) in both in-vitro and in-vivo conditions. Also, we were looking for the differentially expressed genes following the c-fibrosis induction. At the in-vitro condition, primary cardiac fibroblasts were exclusively cultured on collagen-coated or polystyrene plates and, were treated with ISO for fibrosis induction and post-treated or co-treated with DNC. RT-qPCR and flow cytometry analysis indicated that DNC treatment attenuated the fibrotic effect of ISO treatment in these cells. At the in-vivo condition, our findings demonstrated that ISO treatment effectively induces cardiac (and pulmonary) fibrosis, characterized by pro-fibrotic and pro-inflammatory gene expression and IHC (α-SMA, COL1A1, and TGFβ). Interestingly, fibrosis symptoms were reduced following the pretreatment, co-treatment, or post-treatment of DNC with ISO. Additionally, the intensive RNAseq analysis suggested the COMP gene is differentially expressed following the c-fibrosis and our RT-qPCR analysis suggested it as a novel potential marker. Overall, our results promise the application of DNC as a potential preventive or therapy agent before and after heart challenges that lead to c-fibrosis.
Copyright: © 2024 Beikzadeh et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Curcumin reduces cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting myofibroblast differentiation and decreasing transforming growth factor β1 and matrix metalloproteinase 9 / tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1.Chin J Integr Med. 2017 May;23(5):362-369. doi: 10.1007/s11655-015-2159-5. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 26956464
-
Genetic Regulation of Fibroblast Activation and Proliferation in Cardiac Fibrosis.Circulation. 2018 Sep 18;138(12):1224-1235. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.035420. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29950403 Free PMC article.
-
Huoxin Pill inhibits isoproterenol-induced transdifferentiation and collagen synthesis in cardiac fibroblasts through the TGF-β/Smads pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jul 15;275:114061. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114061. Epub 2021 Apr 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33892065
-
Imatinib attenuates cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting platelet-derived growth factor receptors activation in isoproterenol induced model.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 1;12(6):e0178619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178619. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28570599 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin-7-diglucuronide attenuates isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury and fibrosis in mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 Mar;38(3):331-341. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.142. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017. PMID: 28112175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hinderer S, Schenke-Layland K. Cardiac fibrosis–a short review of causes and therapeutic strategies. Advanced drug delivery reviews. 2019;146:77–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

