Molecular identification and studies on genetic diversity and structure-related GC heterogeneity of Spatholobus Suberectus based on ITS2
- PMID: 39384849
- PMCID: PMC11464735
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-75763-w
Molecular identification and studies on genetic diversity and structure-related GC heterogeneity of Spatholobus Suberectus based on ITS2
Abstract
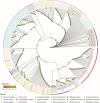
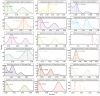
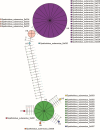
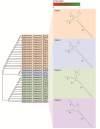
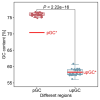
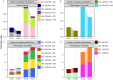
To determine the role of internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2) in the identification of Spatholobus suberectus and explore the genetic diversity of S. suberectus. A total of 292 ITS2s from S. suberectus and 17 other plant species were analysed. S. suberectus was clustered separately in the phylogenetic tree. The genetic distance between species was greater than that within S. suberectus. Synonymous substitution rate (Ks) analysis revealed that ITS2 diverged the most recently within S. suberectus (Ks = 0.0022). These findings suggested that ITS2 is suitable for the identification of S. suberectus. The ITS2s were divided into 8 haplotypes and 4 evolutionary branches on the basis of secondary structure, indicating that there was variation within S. suberectus. Evolutionary analysis revealed that the GC content of paired regions (pGC) was greater than that of unpaired regions (upGC), and the pGC showed a decreasing trend, whereas the upGC remained unchanged. Single-base mutation was the main cause of base pair substitution. In both the initial state and the equilibrium state, the substitution rate of GC was higher than that of AU. The increase in the GC content was partly attributed to GC-biased gene conversion (gBGC). High GC content reflected the high recombination and mutation rates of ITS2, which is the basis for species identification and genetic diversity. We characterized the sequence and structural characteristics of S. suberectus ITS2 in detail, providing a reference and basis for the identification of S. suberectus and its products, as well as the protection and utilization of wild resources.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure-Based GC Investigation Sheds New Light on ITS2 Evolution in Corydalis Species.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 23;24(9):7716. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097716. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175423 Free PMC article.
-
GC heterogeneity reveals sequence-structures evolution of angiosperm ITS2.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Dec 1;23(1):608. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04634-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 38036992 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative and Phylogenetic Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes of Two Medicinal Species of Spatholobus.J AOAC Int. 2023 May 3;106(3):737-747. doi: 10.1093/jaoacint/qsac119. J AOAC Int. 2023. PMID: 36222556
-
Phylogenetic Utility of rRNA ITS2 Sequence-Structure under Functional Constraint.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 3;21(17):6395. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176395. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ITS2 sequence-structure analysis in phylogenetics: a how-to manual for molecular systematics.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2009 Aug;52(2):520-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2009.01.008. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2009. PMID: 19489124 Review.
References
-
- Li, W. et al. Chemical characterization of procyanidins from Spatholobus Suberectus and their antioxidative and anticancer activities. J. Funct. Foods. 12, 468–477 (2015).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GXFS-2021-34/Survey and Collection of Germplasm Resources of Woody & Herbaceous Plants in Guangxi, China
- GXZYA20220013/Self-funded scientific research project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine "Investigation and quality evaluation of germplasm resources of Spatholobus suberectus in Guangxi production areas
- GZSY22-06/Guangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine Appropriate Technology Development and Promotion Project "Optimal solutions for suitable niches for six key protected wild medicinal plants in Guangxi based on photosynthetic characteristics
- No. 27/Guangxi High-Level Key Disciplines Construction Pilot Project in Traditional Chinese Medicine-Authentication of Chinese Medicinal Materials
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

