5-Fluorouracil induces apoptosis in nutritional deprived hepatocellular carcinoma through mitochondrial damage
- PMID: 39379402
- PMCID: PMC11461840
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73143-y
5-Fluorouracil induces apoptosis in nutritional deprived hepatocellular carcinoma through mitochondrial damage
Abstract
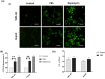
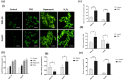
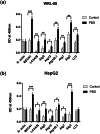
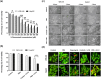
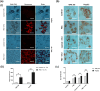
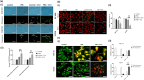
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is the leading chemotherapeutic drug used to treat hepatocellular carcinoma, one of the major cancer diseases after atherosclerosis. Because of chemo-resistance, the success rate of treatment declines with time due to continuous drug exposure. Though autophagy induction is majorly responsible for acquired resistance, the exact role of this evolutionary conserved mechanism is unknown in cancer cell survival and suppression. The usual practice involves the combinatorial use of chemotherapeutic drugs with autophagy inhibitors like Chloroquine and Bafilomycin A, while neglecting the side effects caused by autophagy impairment in healthy cells. Starvation is a well-known physiological inducer of autophagy. In this study, by caloric modulation, we tried to circumvent the resistance imposed by prolonged drug exposure and investigated the effect of 5-FU in nutrient-sufficient and deficient conditions. Our findings show a substantial correlation between autophagy and increased cancer cell death in the presence of 5-FU, with negligible effects on normal cells. Experimental data revealed that nutritional deprivation augmented cell death in the presence of 5-FU through mitochondrial membrane damage and excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, initiating apoptosis. Lipidation study also unveiled that under such combinatorial treatment cellular metabolism shifts from glucose to lipid biosynthesis. Overall, our experimental findings suggest that nutritional deprivation in combination with chemotherapeutic medication can be a new effective strategy to control hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: 5–Fluorouracil; Apoptosis; Autophagy; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Reactive oxygen species (ROS); Starvation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of p53 increases chemosensitivity to 5-FU in nutrient-deprived hepatocarcinoma cells by suppressing autophagy.Cancer Lett. 2014 May 1;346(2):278-84. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.01.011. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24462821
-
Enhancement of anti-tumor effects of 5-fluorouracil on hepatocellular carcinoma by low-intensity ultrasound.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Apr 22;35:71. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0349-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27102814 Free PMC article.
-
Allicin sensitizes hepatocellular cancer cells to anti-tumor activity of 5-fluorouracil through ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway.J Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Aug;131(4):233-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2016.04.017. Epub 2016 Apr 22. J Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27177453
-
Caffeine enhances the anti-tumor effect of 5-fluorouracil via increasing the production of reactive oxygen species in hepatocellular carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2019 Oct 29;36(12):97. doi: 10.1007/s12032-019-1323-8. Med Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31664534
-
The role of ROS-induced autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep;42(4):306-312. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2018.01.005. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29544680 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization, International agency for research on cancer. (2019).
-
- Farshid, P. et al. Repetitive chemoembolization of hypovascular liver metastases from the most common primary sites. Future Oncol. 9, 419–426 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Penchev, D. K., Vladova, L. V., Zashev, M. Z. & Gornev, R. P. Distant liver metastases as a major factor influencing survival in patients with colorectal Cancer. Folia Med. 58, 182 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

