The mechanism and therapeutic strategies in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Role of programmed cell death
- PMID: 39343295
- PMCID: PMC11490929
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cstres.2024.09.001
The mechanism and therapeutic strategies in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Role of programmed cell death
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "The mechanism and therapeutic strategies in doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity: Role of programmed cell death" [Cell Stress Chaperones. 2024;29:666-680].Cell Stress Chaperones. 2024 Dec;29(6):720. doi: 10.1016/j.cstres.2024.10.005. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2024. PMID: 39454443 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
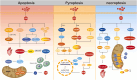
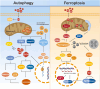
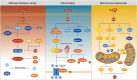
Doxorubicin (DOX) is the most commonly used anthracycline anticancer agent, while its clinical utility is limited by harmful side effects like cardiotoxicity. Numerous studies have elucidated that programmed cell death plays a significant role in DOX-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC). This review summarizes several kinds of programmed cell death, including apoptosis, pyroptosis, necroptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Furthermore, oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction are also important factors in the molecular mechanisms of DIC. Besides, a comprehensive understanding of specific signal pathways of DIC can be helpful to its treatment. Therefore, the related signal pathways are elucidated in this review, including sirtuin deacetylase (silent information regulator 2 [Sir2]) 1 (SIRT1)/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, SIRT1/Klotho, SIRT1/Recombinant Sestrin 2, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, AKT, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. Heat shock proteins function as chaperones, which play an important role in various stressful situations, especially in the heart. Thus, some of heat shock proteins involved in DIC are also included. Hence, the last part of this review focuses on the therapeutic research based on the mechanisms above.
Keywords: Cardiotoxicity; Doxorubicin; Heat shock protein; Programmed cell death; Therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cynaroside regulates the AMPK/SIRT3/Nrf2 pathway to inhibit doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024 Sep 12;25(9):756-772. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2300691. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024. PMID: 39308066 Free PMC article.
-
Qishen granule alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by suppressing ferroptosis via nuclear erythroid factor 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;335:118604. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118604. Epub 2024 Jul 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39047881
-
Therapeutic Targets for DOX-Induced Cardiomyopathy: Role of Apoptosis vs. Ferroptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 26;23(3):1414. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031414. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPK/PGC1α activation by melatonin attenuates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity via alleviating mitochondrial oxidative damage and apoptosis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 Dec;129:59-72. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.032. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 30172748
-
Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: An update on the molecular mechanism and novel therapeutic strategies for effective management.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jul;139:111708. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111708. Epub 2021 May 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34243633 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

