Opacification Kinetics of PLA during Liquid Water Sorption
- PMID: 39339085
- PMCID: PMC11435793
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16182621
Opacification Kinetics of PLA during Liquid Water Sorption
Abstract
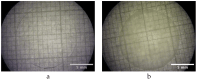
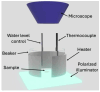
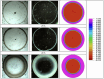
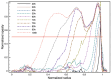
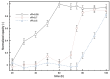
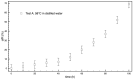
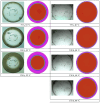
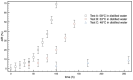
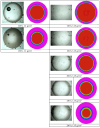
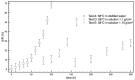
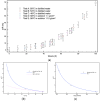
When in contact with water, poly(lactic acid), PLA, undergoes several physical changes. A very evident one is opacification, namely the change from the typical transparent appearance to a white opaque color. This phenomenon is particularly significant for many applications, including packaging, since opacity hinders the possibility of a clear look of the packed goods and also worsens the consumers' perceptions. In this work, we report an analysis of the time evolution of the phenomenon in different conditions of temperature and water concentration. The results allow us to define a time-scale of the phenomenon and to put it in relationship with the temperature and water content inside the material. In particular, opacification proceeds from the outer surface of the specimens toward the center. Both craze formation due to hydrolysis and crystallization contribute to the opacification phenomenon. Opacification becomes faster as temperature increases, whereas the increase in the solution density has the opposite effect. A model for describing the evolution of opacification was proposed and found to be consistent with the experimental data.
Keywords: PLA; diffusion; opacification; water sorption.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An overview of polylactides as packaging materials.Macromol Biosci. 2004 Sep 16;4(9):835-64. doi: 10.1002/mabi.200400043. Macromol Biosci. 2004. PMID: 15468294 Review.
-
Effect of the state of water and relative humidity on ageing of PLA films.Food Chem. 2017 Dec 1;236:109-119. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.113. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28624079
-
Manufacturing and Characterization of Functionalized Aliphatic Polyester from Poly(lactic acid) with Halloysite Nanotubes.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Aug 6;11(8):1314. doi: 10.3390/polym11081314. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31390814 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal degradation behaviour and crystallization kinetics of poly (lactic acid) and cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) based microcellular composite foams.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Oct 15;118(Pt B):1518-1531. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.202. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29981330
-
Poly(lactic acid) stereocomplexes: A decade of progress.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Dec 15;107:97-135. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.04.017. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 27125192 Review.
References
-
- Sari N.H., Suteja S., Sapuan S.M., Ilyas R.A. Bio-Based Packaging: Material, Environmental and Economic Aspects. John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2021. Properties and Food Packaging Application of Poly-(Lactic) Acid. - DOI
-
- Abdelrazek S.G., Abou Taleb E.M.A., Mahmoud A.S., Hamouda T. Utilization of Polylactic Acid (PLA) in Textile Food Packaging: A Review. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022;65:725–738. doi: 10.21608/ejchem.2021.92005.4368. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

