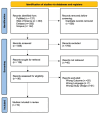
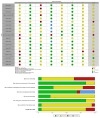
Importance of Coping Strategies on Quality of Life in People with Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39336991
- PMCID: PMC11432133
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13185505
Importance of Coping Strategies on Quality of Life in People with Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurodegenerative disorder of the central nervous system characterized by a variety of symptoms such as fatigue, spasticity, tremors, and cognitive disorders. Individuals with MS may employ different coping strategies to manage these symptoms, which in turn can significantly impact their quality of life (QoL). This review aims to analyze these coping strategies and their impact on QoL. Furthermore, it seeks to identify the key factors that influence the choice and effectiveness of these coping strategies, providing insights into which strategies are most beneficial for enhancing QoL in people with MS. Methods: Systematic searches were performed in Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus databases. This systematic review has been registered in OSF with the number DOI 10.17605/OSF.IO/QY37X. Results: A total of 1192 studies were identified. After reading the full text of the selected studies and applying predefined inclusion criteria, 19 studies were included based on their pertinence and relevance to the topic. The results revealed that emotional variables, demographic factors, personality traits, and family support significantly influence the choice of coping strategies used to manage the symptoms of MS. Problem-solving and task-oriented coping were prevalent among MS patients and associated with better QoL outcomes. Emotional-focused and avoidance strategies were generally linked to poorer QoL, though avoidance provided temporary relief in certain contexts. Social support, emotional health, and cognitive reframing were crucial in enhancing QoL. Conclusions: The findings underscore the importance of tailored psychoeducational and therapeutic interventions focusing on emotional health, social support, and adaptive coping strategies. These interventions can significantly improve the long-term outcomes for individuals with MS. Future research should explore the dynamic interactions between coping strategies and QoL over time, providing a comprehensive understanding of how to best support MS patients in managing their disease.
Keywords: coping strategies; emotional factors; multiple sclerosis; quality of life; rehabilitation; sociodemographic variables.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Social Cognition Deficits on Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis: A Scoping Review.Brain Sci. 2024 Jul 11;14(7):691. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14070691. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39061431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship of coping strategies with mood symptoms, disease related characteristics and demographic variables in patients with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review study.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022 Nov;67:104163. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.104163. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022. PMID: 36126537
-
Characteristics and correlates of coping with multiple sclerosis: a systematic review.Disabil Rehabil. 2019 Feb;41(3):250-264. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2017.1387295. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Disabil Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 28994622
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Coping in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and motor neuron disease: Systematic review.J Clin Nurs. 2021 Jul;30(13-14):1838-1853. doi: 10.1111/jocn.15692. Epub 2021 Feb 19. J Clin Nurs. 2021. PMID: 33555628 Review.
References
-
- McDonald W.I., Compston A., Edan G., Goodkin D., Hartung H., Lublin F.D., McFarland H.F., Paty D.W., Polman C.H., Reingold S.C., et al. Recommended Diagnostic Criteria for Multiple Sclerosis: Guidelines from the International Panel on the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2001;50:121–127. doi: 10.1002/ana.1032. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources