Bibliometric analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma: trends and future directions
- PMID: 39331256
- PMCID: PMC11436492
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01377-3
Bibliometric analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma: trends and future directions
Abstract
Background: Over the past three decades, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has gained considerable attention in the field of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with an increasing number of publications. It is crucial to reveal the global status, research hotspots and future research trends of ER stress in HCC. The aim of this study is to analyze the publications related to ER stress in HCC through bibliometric analysis in order to better understand the current status of ER stress research in HCC and to identify potential new research directions.
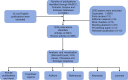
Methods: In this study, articles and reviews on ER stress in HCC up to December 31, 2023 were searched and downloaded from the Science Citation Index-Expanded (SCIE) of the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC), Pubmed, Scopus and Embase databases. Using CiteSpace 6.2.R6, VOSviewer 1.6.19, Scimago Graphica and Microsoft Office Excel 2019, the knowledge networks of a variety of countries, regions, authors, references, keywords and journals were analyzed.
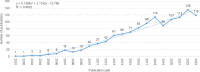
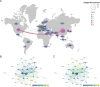
Results: A total of 1239 publications were retrieved, including 843 articles and 396 review articles. The number of global publications is increasing every year, with the majority of publications coming from China and the USA. Ih-Jen Su, Wenya Huang and Wei Wei are the top 3 prolific authors. "Progression", "inflammation", "cell cycle arrest", "metabolism", "snsignaling pathways", "pathogenesis" and "non-alcoholic fatty liver disease" have emerged as research hotspots in recent years. The journal with the greatest co-citation is Hepatology.
Conclusions: Based on current global trends, the total number of publications on ER stress in HCC research will continue to increase, but there is a need for more cooperation between authors and countries/regions. ER stress in HCC will continue to be a research priority.
Conclusions: Based on current global trends, the total number of publications on ER stress in HCC research will continue to increase, but there is a need for more cooperation between authors and countries/regions. ER stress in HCC will continue to be a research priority.
Keywords: Bibliometrics; Endoplasmic reticulum; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Research trends; Stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Telomerase-related advances in hepatocellular carcinoma: A bibliometric and visual analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 7;30(9):1224-1236. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1224. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38577190 Free PMC article.
-
Research landscape and frontiers of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 12;14:1240649. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1240649. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37771721 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric study of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1210802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1210802. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Bibliometric analysis of global research trends on male osteoporosis: a neglected field deserves more attention.Arch Osteoporos. 2021 Oct 11;16(1):154. doi: 10.1007/s11657-021-01016-2. Arch Osteoporos. 2021. PMID: 34632530 Review.
References
-
- Wang Y, Deng B. Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanism, targeted therapy, and biomarkers. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023;42(3):629–52. 10.1007/s10555-023-10084-4. - PubMed
-
- Asafo-Agyei KO, Samant H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. StatPearls. St. Petersburg: StatPearls Publishing; 2023. - PubMed
-
- Divya S, Ravanan P. Cellular battle against endoplasmic reticulum stress and its adverse effect on health. Life Sci. 2023;323:121705. 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121705. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
