Can Cytoreductive Nephrectomy Improve Outcomes of Nivolumab Treatment in Patients with Metastatic Clear-Cell Renal Carcinoma?
- PMID: 39330012
- PMCID: PMC11431784
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol31090384
Can Cytoreductive Nephrectomy Improve Outcomes of Nivolumab Treatment in Patients with Metastatic Clear-Cell Renal Carcinoma?
Abstract
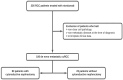
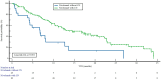
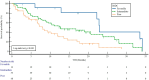
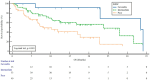
Background: This study aimed to investigate the effect of cytoreductive nephrectomy (CN) on the survival outcomes of nivolumab used as a subsequent therapy after the failure of at least one anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agent in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Methods: We included 106 de novo metastatic ccRCC patients who received nivolumab after progression on at least one anti-VEGF agent. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was performed to investigate the factors affecting survival in patients receiving nivolumab. Results: Of the 106 de novo metastatic ccRCC patients, 83 (78.3%) underwent CN. There were no statistical differences between the two groups in terms of age, gender, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) score, tumor size, International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) risk group, number of previous treatment lines, first-line anti-VEGF therapy, or metastasis sites (p = 0.137, p = 0.608, p = 0.100, p = 0.376, p = 0.185, p = 0.776, p = 0.350, and p = 0.608, respectively). The patients who received nivolumab with CN had a longer time to treatment discontinuation (TTD) [14.5 months, 95% confidence interval (CI): 8.6-20.3] than did those without CN 6.7 months (95% CI: 3.9-9.5) (p = 0.001). The median overall survival (OS) was 22.7 months (95% CI: 16.1-29.4). The patients with CN had a median OS of 22.9 months (95% CI: 16.3-29.4), while those without CN had a median OS of 8.1 months (95% CI: 5.6-10.5) (p = 0.104). In the multivariate analysis, CN [hazard ratio (HR): 0.521; 95% CI: 0.297-0.916; p = 0.024] and the IMDC risk score (p = 0.011) were statistically significant factors affecting TTD; however, the IMDC risk score (p = 0.006) was the only significant factor for overall survival. Conclusions: Our study showed that the TTD of nivolumab was longer in metastatic ccRCC patients who underwent cytoreductive nephrectomy.
Keywords: clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma; cytoreductive nephrectomy; nivolumab; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Timing of Immunotherapy and Cytoreductive Nephrectomy in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Real-World Data on Survival Outcomes from the CKCis Database.Curr Oncol. 2024 Aug 18;31(8):4704-4712. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31080351. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39195334 Free PMC article.
-
First-line therapy for adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 4;5(5):CD013798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013798.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37146227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Impact of IMDC Category Shift From Baseline to Nivolumab Initiation in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Sub-Analysis of the MEET-URO 15 Study.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2025 Feb;23(1):102267. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2024.102267. Epub 2024 Nov 10. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39603144
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erratum: Eyestalk Ablation to Increase Ovarian Maturation in Mud Crabs.J Vis Exp. 2023 May 26;(195). doi: 10.3791/6561. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37235796
References
-
- Garfield K., Lagrange C.A. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. [(accessed on 1 January 2024)]. Renal cell cancer. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470336. - PubMed
-
- Khan M.M.R., Hassan M.R., Rahman F., Chowdhury A.M. Clinicopathological Study of Renal Cell Carcinoma-A Study of 100 Cases. Ibrahim Card. Med. J. 2018;8:17–22. doi: 10.3329/icmj.v8i1-2.53971. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

