Targeting the p90RSK/MDM2/p53 Pathway Is Effective in Blocking Tumors with Oncogenic Up-Regulation of the MAPK Pathway Such as Melanoma and Lung Cancer
- PMID: 39329730
- PMCID: PMC11430938
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13181546
Targeting the p90RSK/MDM2/p53 Pathway Is Effective in Blocking Tumors with Oncogenic Up-Regulation of the MAPK Pathway Such as Melanoma and Lung Cancer
Abstract
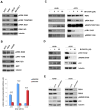
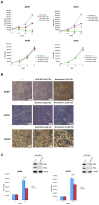
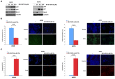
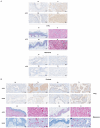
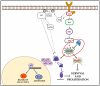
In most human tumors, the MAPK pathway is constitutively activated. Since p90RSK is downstream of MAPK, it is often hyperactive and capable of phosphorylating oncogenic substrates. We have previously shown that p90RSK phosphorylates MDM2 at S166, promoting p53 degradation in follicular thyroid carcinomas. Thus, the inhibition of p90RSK restores p53 expression, which in turn inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. In the present study, we demonstrated that the p90RSK/MDM2/p53 pathway proved to be an excellent target in the therapy of tumors with MAPK hyperactivation. For this purpose, we selected p53wt melanoma, lung and medullary thyroid carcinoma cell lines with high activation of p90RSK. In these cell lines, we demonstrated that the p90RSK/MDM2/p53 pathway is implicated in the regulation of the cell cycle and apoptosis through p53-dependent transcriptional control of p21 and Bcl-2. Furthermore, with an immunohistochemical evaluation of primary melanomas and lung tumors, which exhibit highly activated p90RSK compared to corresponding normal tissue, we demonstrated that MDM2 stabilization was associated with p90RSK phosphorylation. The results indicate that p90RSK is able to control the proliferative rate and induction of apoptosis through the regulation of p53wt levels by stabilizing MDM2 in selected tumors with constitutively activated MAPKs, making p90RSK a new attractive target for anticancer therapy.
Keywords: MDM2; apoptosis; cancer; cancer drug resistance; cell proliferation; p53; p90RSK; targeted therapy; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
p90RSK Regulates p53 Pathway by MDM2 Phosphorylation in Thyroid Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;15(1):121. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010121. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612117 Free PMC article.
-
SPARC functions as an anti-stress factor by inactivating p53 through Akt-mediated MDM2 phosphorylation to promote melanoma cell survival.Oncogene. 2011 Dec 8;30(49):4887-900. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.198. Epub 2011 Jun 20. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21685937
-
p38 MAPK-induced MDM2 degradation confers paclitaxel resistance through p53-mediated regulation of EGFR in human lung cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 16;7(7):8184-99. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6945. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26799187 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the p53-MDM2 interaction by adenovirus delivery of ribosomal protein L23 stabilizes p53 and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer.J Gene Med. 2010 Feb;12(2):147-56. doi: 10.1002/jgm.1424. J Gene Med. 2010. PMID: 20020415
-
Mdm2 links genotoxic stress and metabolism to p53.Protein Cell. 2010 Dec;1(12):1063-72. doi: 10.1007/s13238-010-0140-9. Epub 2011 Jan 8. Protein Cell. 2010. PMID: 21213101 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Drosten M., Sum E.Y.M., Lechuga C.G., Simón-Carrasco L., Jacob H.K.C., García-Medina R., Huang S., Beijersbergen R.L., Bernards R., Barbacid M. Loss of P53 Induces Cell Proliferation via Ras-Independent Activation of the Raf/Mek/Erk Signaling Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:15155–15160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417549111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

