Rational Design of Dual-Domain Binding Inhibitors for N-Acetylgalactosamine Transferase 2 with Improved Selectivity over the T1 and T3 Isoforms
- PMID: 39328774
- PMCID: PMC11423303
- DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00633
Rational Design of Dual-Domain Binding Inhibitors for N-Acetylgalactosamine Transferase 2 with Improved Selectivity over the T1 and T3 Isoforms
Abstract
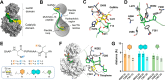
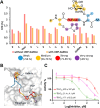
The GalNAc-transferase (GalNAc-T) family, consisting of 20 isoenzymes, regulates the O-glycosylation process of mucin glycopeptides by transferring GalNAc units to serine/threonine residues. Dysregulation of specific GalNAc-Ts is associated with various diseases, making these enzymes attractive targets for drug development. The development of inhibitors is key to understanding the implications of GalNAc-Ts in human diseases. However, developing selective inhibitors for individual GalNAc-Ts represents a major challenge due to shared structural similarities among the isoenzymes and some degree of redundancy among the natural substrates. Herein, we report the development of a GalNAc-T2 inhibitor with higher potency compared to those of the T1 and T3 isoforms. The most promising candidate features bivalent GalNAc and thiophene moieties on a peptide chain, enabling binding to both the lectin and catalytic domains of the enzyme. The binding mode was confirmed by competitive saturation transfer difference NMR experiments and validated through molecular dynamics simulations. The inhibitor demonstrated an IC50 of 21.4 μM for GalNAc-T2, with 8- and 32-fold higher selectivity over the T3 and T1 isoforms, respectively, representing a significant step forward in the synthesis of specific GalNAc-T inhibitors tailored to the unique structural features of the targeted isoform.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The lectin domain of the polypeptide GalNAc transferase family of glycosyltransferases (ppGalNAc Ts) acts as a switch directing glycopeptide substrate glycosylation in an N- or C-terminal direction, further controlling mucin type O-glycosylation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 5;288(27):19900-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.477877. Epub 2013 May 20. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23689369 Free PMC article.
-
Mucin-type O-glycosylation is controlled by short- and long-range glycopeptide substrate recognition that varies among members of the polypeptide GalNAc transferase family.Glycobiology. 2016 Apr;26(4):360-76. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwv108. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Glycobiology. 2016. PMID: 26610890 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Analysis of a GalNAc-T2 Mutant Reveals an Induced-Fit Catalytic Mechanism for GalNAc-Ts.Chemistry. 2018 Jun 12;24(33):8382-8392. doi: 10.1002/chem.201800701. Epub 2018 May 16. Chemistry. 2018. PMID: 29601100
-
Recent structural and mechanistic insights into protein O-GalNAc glycosylation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Feb;44(1):61-7. doi: 10.1042/BST20150178. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 26862189 Review.
-
Polypeptide GalNAc-Ts: from redundancy to specificity.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019 Jun;56:87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2018.12.007. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 30703750 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
