Effect of Mediterranean diet on body mass index and fatigue severity in patients with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
- PMID: 39323842
- PMCID: PMC11422037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37705
Effect of Mediterranean diet on body mass index and fatigue severity in patients with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Recent studies imply that Mediterranean Diet (MeD) may play an important role in the management of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of MeD in addressing MS-related complications.
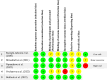
Methods: A thorough search was performed in MEDLINE (PubMed), Scopus, EMBASE, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, Web of Science, and the Central Cochrane Library, covering trials published until September 2023. The quantitative data were synthesized using random effect models through STATA14.
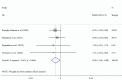
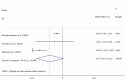
Results: After analyzing 228 entries, we found five Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) with a total of 540 participants, who had an average disease duration of 8.5 years. The combined effect size revealed a decrease in Body Mass Index (BMI) (Weighted Mean Difference [WMD] = -0.88 kg/m2; 95 % Confidence Interval [CI] = -1.68, -0.08; P = 0.030). There was also a non-significant marginal improvement in fatigue severity (WMD = -8.29; 95 % CI = -16.74, 0.16; P = 0.054).
Conclusion: Adherence to MeD may improve BMI and fatigue severity in MS patients. Further RCTs are needed to confirm the current results.
Keywords: Fatigue; Mediterranean diet; Meta‐analysis; Multiple sclerosis; Systematic review.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of subcutaneous dulaglutide on weight loss in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur J Clin Invest. 2024 Apr;54(4):e14125. doi: 10.1111/eci.14125. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 37950521
-
Effects of exercise in people with multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Public Health. 2024 Apr 10;12:1387658. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1387658. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38660348 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term impact of mediterranean diet on cardiovascular disease prevention: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 May;49(5):102509. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102509. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38431146 Review.
-
Efficacy of diet on fatigue, quality of life and disability status in multiple sclerosis patients: rapid review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Neurol. 2022 Oct 20;22(1):388. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02913-w. BMC Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36266639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moravejolahkami A.R., Paknahad Z., Chitsaz A. Dietary intake of energy and fiber in MS patients; an approach to prebiotics role. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019;49(6):1039–1050. doi: 10.1108/nfs-01-2019-0001. - DOI
-
- Bohlouli J., Namjoo I., Borzoo-Isfahani M., Poorbaferani F., Moravejolahkami A.R., Clark C.C.T., et al. Modified Mediterranean diet v. traditional Iranian diet: efficacy of dietary interventions on dietary inflammatory index score, fatigue severity and disability in multiple sclerosis patients. Br. J. Nutr. 2022;128(7):1274–1284. doi: 10.1017/S000711452100307X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Martínez-González M.A. Should we remove wine from the Mediterranean diet?: a narrative review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024;119(2):262–270. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

