Optimized method for higher yield of alveolar macrophage isolation for ex vivo studies
- PMID: 39319125
- PMCID: PMC11419857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37221
Optimized method for higher yield of alveolar macrophage isolation for ex vivo studies
Abstract
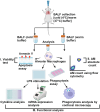
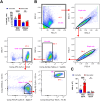
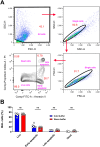
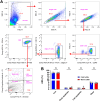
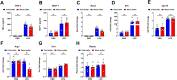
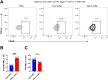
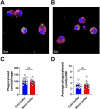
Alveolar macrophages (AMs) are a fully differentiated lung-resident immune cell population and are a critical component of lung immunity. AMs can be easily isolated from mice via bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) collection. The quality and quantity of AMs in BALF isolation are critical for generating reliable and high-quality data for ex vivo studies. Traditional techniques use ice-cold (4°C) buffer to collect AMs in BALF and result in low yield. Hence, a new method that consistently gives a higher yield of AMs is needed. We demonstrate here an optimized method that significantly increases the quantity of AM recovery in BALF (>2.8 times than the traditional method). Our method uses a warm-buffer (37°C) containing EDTA. We compared the viability and functional parameters (cytokine/chemokine expression, phagocytosis) of AMs isolated by our new and traditional methods. Our study revealed that AMs collected using our method have similar viability and functional characteristics to those collected using traditional method. Hence, our new method can be used for the collection of a higher number of AMs without altering their function. This protocol might also be useful for isolating tissue-resident immune cells from other anatomical sites for ex vivo and other downstream applications.
Keywords: Alveolar macrophages; Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; Immune response; Phagocytosis; Warm buffer.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of injection buffer volume to perform bronchoalveolar lavage fluid collection for isolating alveolar macrophages to investigate fine particle-induced IL-1α secretion.J Immunotoxicol. 2021 Dec;18(1):163-172. doi: 10.1080/1547691X.2021.1979699. J Immunotoxicol. 2021. PMID: 34761701
-
Corticosteroids alter alveolar macrophage control of Lichtheimia corymbifera spores in an ex vivo mouse model.Med Mycol. 2021 Jul 6;59(7):694-700. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myaa104. Med Mycol. 2021. PMID: 33369666
-
ISM1 protects lung homeostasis via cell-surface GRP78-mediated alveolar macrophage apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jan 25;119(4):e2019161119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2019161119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35046017 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar Epithelial Cells Promote IGF-1 Production by Alveolar Macrophages Through TGF-β to Suppress Endogenous Inflammatory Signals.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 21;11:1585. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01585. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32793225 Free PMC article.
-
[Deep lung--cellular reaction to HIV].Rev Port Pneumol. 2007 Mar-Apr;13(2):175-212. Rev Port Pneumol. 2007. PMID: 17492233 Review. Portuguese.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

