Mendelian randomization provides causal association between COVID-19 and thyroid cancer: insights from a multi-cancer analysis
- PMID: 39319057
- PMCID: PMC11419959
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1419020
Mendelian randomization provides causal association between COVID-19 and thyroid cancer: insights from a multi-cancer analysis
Abstract
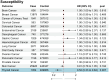
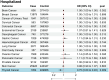
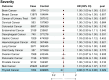
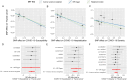
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the SARS-CoV-2 virus has caused over 600 million confirmed infections and more than 6.8 million deaths worldwide, with ongoing implications for human health. COVID-19 has been extensively documented to have extrapulmonary manifestations due to the widespread expression of necessary ACE2 receptors in the human body. Nevertheless, the association between COVID-19 and cancer risk remains inadequately explored. This study employs Mendelian randomization (MR) methods to examine the causal relationship between genetic variations associated with COVID-19 and the risk of developing cancer. The findings indicate that COVID-19 has negligible impact on most cancer risks. Interestingly, a higher COVID-19 impact is associated with a decreased risk of thyroid cancer. In summary, our findings demonstrate a genetic correlation between COVID-19 and thyroid cancer, contributing to our understanding of the interplay between COVID-19 and cancer risk.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mendelian randomization; SARS-CoV-2; cancer risk; thyroid.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Du, Ma, Cai, Liu and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of lipid-lowering drugs with COVID-19 outcomes from a Mendelian randomization study.Elife. 2021 Dec 6;10:e73873. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73873. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34866576 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and Thyroid Function: A Bi-Directional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study.Thyroid. 2022 Sep;32(9):1037-1050. doi: 10.1089/thy.2022.0243. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Thyroid. 2022. PMID: 35734897
-
The causal relationship between COVID-19 and seventeen common digestive diseases: a two-sample, multivariable Mendelian randomization study.Hum Genomics. 2023 Sep 26;17(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s40246-023-00536-x. Hum Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37752570 Free PMC article.
-
The possible causal relationship between COVID-19 and imaging markers of cerebral small vessel disease: a Mendelian randomization study.Neurol Res. 2024 Aug;46(8):735-742. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2024.2349440. Epub 2024 May 2. Neurol Res. 2024. PMID: 38695379
-
Insights from Mendelian randomization and genetic correlation analyses into the relationship between endometriosis and its comorbidities.Hum Reprod Update. 2023 Sep 5;29(5):655-674. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmad009. Hum Reprod Update. 2023. PMID: 37159502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) situation reports (2023). Available online at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... (Accessed October 07, 2023)
-
- CSSEGISandData . COVID-19 Data Repository by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (2023). Available online at: https://github.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19 (Accessed October 6, 2023).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

