Deciphering the Role of LncRNAs in Osteoarthritis: Inflammatory Pathways Unveiled
- PMID: 39318993
- PMCID: PMC11421445
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S489682
Deciphering the Role of LncRNAs in Osteoarthritis: Inflammatory Pathways Unveiled
Abstract
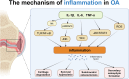
Long non-coding RNA (LncRNA), with transcripts over 200 nucleotides in length, play critical roles in numerous biological functions and have emerged as significant players in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA), an inflammatory condition traditionally viewed as a degenerative joint disease. This review comprehensively examines the influence of LncRNA on the inflammatory processes driving OA progression, focusing on their role in regulating gene expression, cellular activities, and inflammatory pathways. Notably, LncRNAs such as MALAT1, H19, and HOTAIR are upregulated in OA and exacerbate the inflammatory milieu by modulating key signaling pathways like NF-κB, TGF-β/SMAD, and Wnt/β-catenin. Conversely, LncRNA like MEG3 and GAS5, which are downregulated in OA, show potential in dampening inflammatory responses and protecting against cartilage degradation by influencing miRNA interactions and cytokine production. By enhancing our understanding of LncRNA' roles in OA inflammation, we can better leverage them as potential biomarkers for the disease and develop innovative therapeutic strategies for OA management. This paper aims to delineate the mechanisms by which LncRNA influence inflammatory responses in OA and propose them as novel targets for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: LncRNA; chondrocytes; inflammation; osteoarthritis; pro-inflammatory factors.
© 2024 Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA MEG3 Inhibits the Degradation of the Extracellular Matrix of Chondrocytes in Osteoarthritis via Targeting miR-93/TGFBR2 Axis.Cartilage. 2021 Dec;13(2_suppl):1274S-1284S. doi: 10.1177/1947603519855759. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 31253047 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of lncRNAs in osteoarthritis: An updated review.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 11;13:982773. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.982773. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36304464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A long non-coding RNA, HOTAIR, promotes cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting WIF-1 expression and activating Wnt pathway.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Jul 10;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12860-020-00299-6. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32650720 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of lncRNAs in chondrocytes from osteoarthritis patients.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110642. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110642. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32927251 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes osteoarthritis progression via miR-17-5p/FUT2/β-catenin axis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jun 15;9(7):711. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0746-z. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29907764 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

