The m6A reader YTHDC2 promotes the pathophysiology of temporal lobe epilepsy by modulating SLC7A11-dependent glutamate dysregulation in astrocytes
- PMID: 39310099
- PMCID: PMC11413790
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.100703
The m6A reader YTHDC2 promotes the pathophysiology of temporal lobe epilepsy by modulating SLC7A11-dependent glutamate dysregulation in astrocytes
Abstract
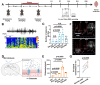
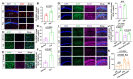
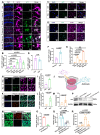
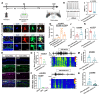
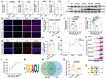
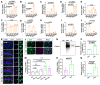
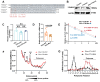
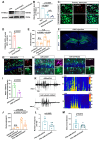
Rationale: Epilepsy affects over 70 million people globally, with temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis (TLE-HS) often progressing to a drug-resistant state. Recent research has highlighted the role of reactive astrocytes and glutamate dysregulation in epilepsy pathophysiology. This study aims to investigate the involvement of astrocytic xCT, a glutamate-cystine antiporter, and its regulation by the m6A reader protein YTHDC2 in TLE-HS. Methods: A pilocarpine-induced epilepsy model in mice was used to study the role of xCT in reactive astrocytes. The expression of xCT and its regulation by YTHDC2 were assessed through various molecular and cellular techniques. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blotting were used to measure mRNA and protein levels of xCT and YTHDC2, respectively; immunofluorescence was utilized to visualize their localization and expression in astrocytes. In vivo glutamate measurements were conducted using microdialysis to monitor extracellular glutamate levels in the hippocampus. RNA immunoprecipitation-qPCR (RIP-qPCR) was performed to investigate the binding of YTHDC2 to SLC7A11 mRNA, while methylated RNA immunoprecipitation-qPCR (MeRIP-qPCR) was performed to quantify m6A modifications on SLC7A11 mRNA. A dual-luciferase reporter assay was conducted to assess the effect of m6A modifications on SLC7A11 mRNA translation, and polysome profiling was employed to evaluate the translational efficiency of SLC7A11 mRNA. Inhibition experiments involved shRNA-mediated knockdown of SLC7A11 (commonly known as xCT) and YTHDC2 expression in astrocytes. Video-electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings were used to monitor seizure activity in mice. Results: The xCT transporter in reactive astrocytes significantly contributes to elevated extracellular glutamate levels, enhancing neuronal excitability and seizure activity. Increased xCT expression is influenced by the m6A reader protein YTHDC2, which regulates its expression through m6A methylation. Inhibition of xCT or YTHDC2 in astrocytes reduces glutamate levels and effectively controls seizures in a mouse model. Specifically, mice with SLC7A11- or YTHDC2-knockdown astrocytes showed decreased glutamate concentration in the hippocampus and reduced frequency and duration of epileptic seizures. Conclusions: This study highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting YTHDC2 and xCT in reactive astrocytes to mitigate epilepsy. The findings provide a novel perspective on the mechanisms of glutamate dysregulation and their implications in seizure pathophysiology, suggesting that modulation of YTHDC2 and xCT could be a promising strategy for treating TLE.
Keywords: epilepsy; glutamate dysregulation; hippocampal sclerosis; m6A methylation; reactive astrocytes.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The N6-methyladenosine modification enhances ferroptosis resistance through inhibiting SLC7A11 mRNA deadenylation in hepatoblastoma.Clin Transl Med. 2022 May;12(5):e778. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.778. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35522946 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 1β Regulation of the System xc- Substrate-specific Subunit, xCT, in Primary Mouse Astrocytes Involves the RNA-binding Protein HuR.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 22;291(4):1643-1651. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.697821. Epub 2015 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26601945 Free PMC article.
-
The cystine-glutamate exchanger (xCT, Slc7a11) is expressed in significant concentrations in a subpopulation of astrocytes in the mouse brain.Glia. 2018 May;66(5):951-970. doi: 10.1002/glia.23294. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Glia. 2018. PMID: 29350434
-
Glial Glutamate Transporter-Mediated Plasticity: System xc-/xCT/SLC7A11 and EAAT1/2 in Brain Diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Mar 20;28(3):57. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2803057. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37005761 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Excessive Extracellular Glutamate Accumulation in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.Neurochem Res. 2017 Jun;42(6):1724-1734. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2105-8. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 27873132 Review.
References
-
- Thijs RD, Surges R, O'Brien TJ, Sander JW. Epilepsy in adults. Lancet. 2019;393:689–701. - PubMed
-
- Asadi-Pooya AA, Brigo F, Lattanzi S, Blumcke I. Adult epilepsy. Lancet. 2023;402:412–424. - PubMed
-
- Perucca E, Perucca P, White HS, Wirrell EC. Drug resistance in epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22:723–734. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

